Learning how to shoot high frame rate videos unlocks the potential to create visually dynamic and captivating footage. This technique is essential for capturing fast-moving scenes with clarity and smoothness, making it a valuable skill for videographers aiming to elevate their craft. Whether for cinematic effects, scientific analysis, or sports coverage, mastering high frame rate filming opens new creative avenues.
This guide covers the fundamental concepts, camera settings, equipment requirements, lighting techniques, recording procedures, and post-production tips necessary to achieve high-quality high frame rate videos. Understanding these elements ensures optimal results and enhances the storytelling impact of your footage.
Overview of Shooting High Frame Rate Video
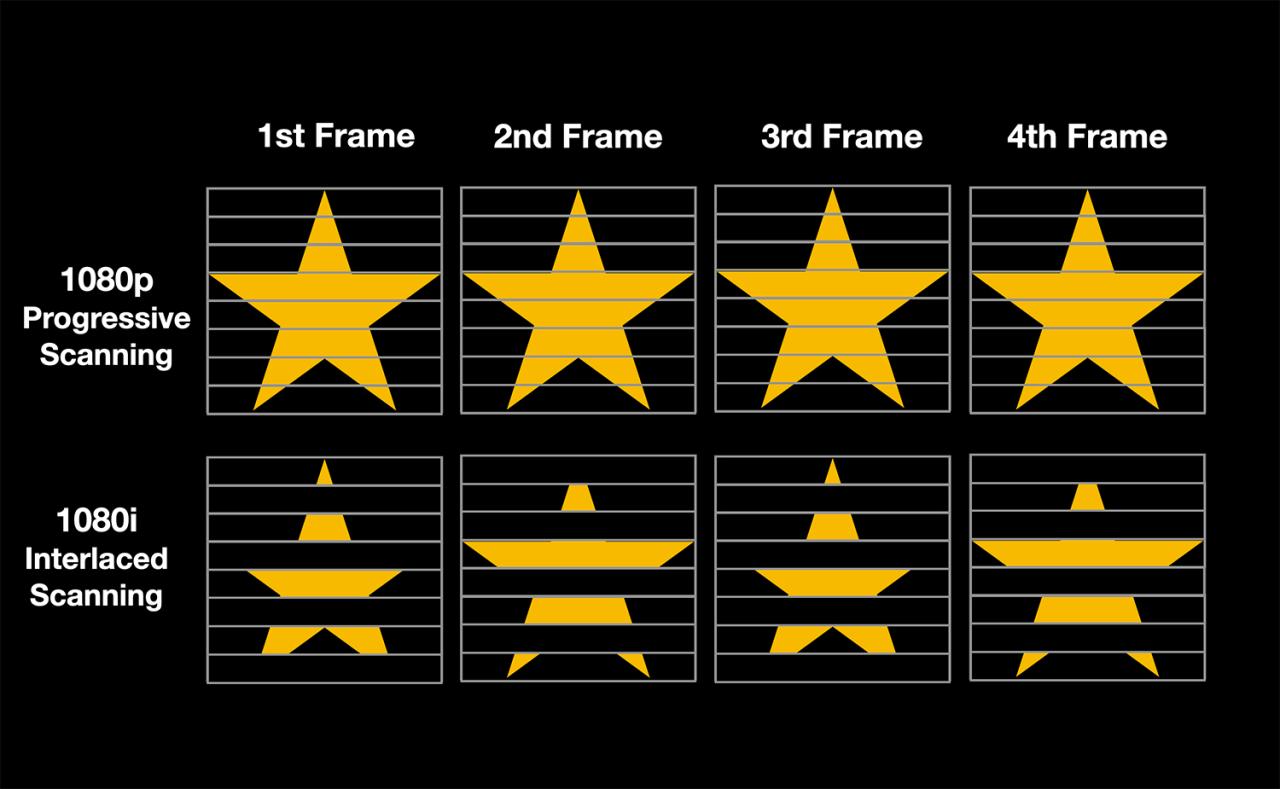
High frame rate (HFR) video recording has become a pivotal technique in modern videography, offering filmmakers and content creators the ability to capture fast-moving scenes with exceptional clarity and smoothness. Unlike standard frame rates, HFR captures a greater number of frames per second, enabling more detailed slow-motion playback and enhanced visual storytelling. This approach is increasingly employed across various industries, including sports broadcasting, cinematic productions, and scientific research, where precise motion portrayal is essential.
Understanding the fundamentals of high frame rate filming involves exploring the typical frame rates used, how they differ from standard recordings, and the technical considerations that influence their implementation. This knowledge helps creators optimize their footage for clarity, realism, and artistic effect, ensuring that high-speed scenes are rendered with the highest quality possible.
Typical Frame Rates Used in High-Speed Videography
High-speed videography relies on capturing motion at frame rates significantly higher than conventional standards. These elevated frame rates are crucial for slow-motion analysis and for producing smooth, detailed playback of rapid movements. Common frame rates include:
- 120 fps (frames per second): Often used in sports broadcasting and cinematic slow-motion sequences, providing a good balance between smoothness and manageable data size.
- 240 fps: Suitable for more detailed slow-motion footage, capturing fast actions like dance moves, sports techniques, or mechanical movements with greater clarity.
- 1000 fps and above: Employed in specialized scientific or industrial applications where capturing extremely rapid phenomena, such as bullet trajectories or fluid dynamics, is necessary. These frame rates generate enormous data and require robust recording equipment and processing power.
Choosing the appropriate high frame rate depends on the desired slow-motion effect, the speed of the subject, and technical considerations such as storage capacity and camera capabilities.
Comparison of Standard and High Frame Rate Recordings
To better understand the benefits and differences between standard and high frame rate video, the following table highlights key aspects:
| Feature | Standard Frame Rate | High Frame Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Typical Frame Rates | 24 fps, 30 fps | 120 fps, 240 fps, 1000 fps or higher |
| Motion Smoothness | Less smooth for fast motion; may appear choppy when slowed down | Extremely smooth, ideal for slow-motion playback |
| Data Storage Requirements | Lower data rate; easier to store and process | Much higher data rate; demands advanced storage solutions |
| Application Focus | Standard video production, live broadcasts, online content | Slow-motion effects, scientific analysis, high-speed sports |
| Camera and Equipment | Wider availability; more affordable options | Specialized high-speed cameras; more expensive and complex setup |
Adopting high frame rate filming enhances visual storytelling by offering fluid motion capture that reveals details often overlooked in standard recordings. It requires careful planning, suitable equipment, and consideration of storage and processing capabilities, but the results significantly elevate the quality and impact of visual content.
Camera Settings for High Frame Rate Shooting

Capturing high frame rate footage requires precise camera settings to ensure clarity, sharpness, and smooth motion portrayal. Selecting appropriate camera specifications and optimizing key parameters such as shutter speed, ISO, and aperture are essential for achieving professional-quality slow-motion videos or fast-action sequences. Understanding these settings allows videographers to adapt to various shooting scenarios, lighting conditions, and camera models, ensuring optimal results while maintaining image quality.
Properly configured camera settings help prevent issues like motion blur, noise, or underexposure, which can compromise the visual integrity of high frame rate footage. This section provides guidance on the essential camera specifications and detailed recommended settings tailored for different scenarios and camera models to facilitate high-quality slow-motion recording.
Camera Specifications and Features for High Frame Rate Capture
Choosing a camera with suitable specifications is foundational for successful high frame rate videography. Essential features include:
- High-resolution sensor: Ensures detailed and sharp images even when slowed down during playback.
- High frame rate capabilities: Support for recording at least 120 fps, with some models offering up to 240 fps or higher.
- Fast readout speeds: Reduces rolling shutter artifacts, ensures smooth motion capture, and minimizes motion artifacts.
- Good low-light performance: Enables shooting in varied lighting conditions with minimal noise, crucial when increasing ISO.
- Robust stabilization features: To counteract camera shake during high-speed recording.
In addition, advanced features such as customizable shutter angle, extensive ISO range, and high-quality lenses enhance the flexibility and quality of high frame rate footage. Cameras designed specifically for slow-motion work, like the Sony FX6, Canon EOS C300 Mark III, or RED Komodo, often include dedicated high frame rate modes that simplify setting adjustments and optimize internal processing.
Optimal Shutter Speed, ISO, and Aperture Settings for High Frame Rate Footage
Adjusting shutter speed, ISO, and aperture accordingly is vital for achieving the desired motion clarity, exposure, and image sharpness during high frame rate recording. The key considerations include:
Shutter Speed: The general rule for smooth motion is to set the shutter speed at double the frame rate. For example, at 120 fps, set the shutter speed to around 1/240 seconds. This maintains natural motion blur, preventing the footage from appearing unnaturally crisp or jittery.
ISO: Use the lowest ISO possible to reduce noise. High ISO settings can introduce grain, especially in low-light conditions, compromising image quality. When shooting in bright environments, ISO can typically be kept at base levels; in darker conditions, incremental increases are acceptable while monitoring noise levels.
Aperture: The aperture controls depth of field and exposure. Adjust aperture to achieve proper exposure based on lighting conditions while maintaining sufficient depth of field. Larger apertures (smaller f-number) allow more light in but reduce depth of field; smaller apertures (larger f-number) do the opposite.
Recommended Settings for Various Camera Models and Scenarios
To assist in practical application, the following table illustrates recommended camera settings across popular models and typical shooting scenarios:
| Camera Model | Scenario | Frame Rate (fps) | Shutter Speed | ISO Range | Aperture |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sony FX6 | Indoor Sports | 120 | 1/240 sec | 800–3200 | f/2.8–f/5.6 |
| Canon EOS C300 Mark III | Outdoor Action | 180 | 1/360 sec | 100–3200 | f/4–f/8 |
| RED Komodo | Slow Motion in Well-Lit Environment | 240 | 1/480 sec | 200–800 | f/2.8–f/4 |
| Entry-Level DSLR (e.g., Canon EOS 90D) | Studio or Controlled Lighting | 120 | 1/240 sec | 100–6400 | f/3.5–f/8 |
It is essential to adapt these settings based on lighting conditions and specific scene requirements. For instance, in low-light environments, increasing ISO and opening the aperture can compensate for reduced light, whereas in brightly lit scenes, lowering ISO and using smaller apertures help prevent overexposure. Monitoring and adjusting these parameters in real-time enhances overall footage quality and ensures the desired cinematic effect in high frame rate recordings.
Equipment and Accessories Needed
Shooting high frame rate videos demands specific equipment that ensures clarity, stability, and optimal performance. Selecting the right gear is crucial to capturing smooth, detailed footage at elevated frame rates, which often requires handling increased data flow and maintaining consistent image quality. This section discusses the essential tools and accessories that professionals and enthusiasts should consider when preparing for high frame rate videography.High frame rate recording pushes the limits of standard equipment, necessitating specialized hardware to achieve desirable results.
The right camera, lenses, and stabilization tools not only facilitate capturing fast-moving action with precision but also prevent issues like motion blur, jitter, or focus inconsistency. Complementary accessories further enhance recording quality by addressing lighting, data management, and stabilization challenges encountered during high-speed shooting.
Essential Equipment for High Frame Rate Shooting
Effective high frame rate videography hinges on the selection of specific equipment tailored for high-speed capture. Below are core components that form the foundation of successful high frame rate recording setups.
- High-Speed Cameras: Cameras specifically designed for high frame rate recording can capture thousands of frames per second. Examples include the Phantom series by Vision Research, capable of shooting at up to 100,000 fps for ultra-slow-motion analysis. These cameras typically feature large sensors, high data throughput, and specialized chips optimized for rapid image processing.
- Lenses: Fast, high-quality lenses such as prime lenses with wide apertures (e.g., f/1.4 or f/2.8) are preferred to allow ample light into the sensor, compensating for the reduced exposure times at high fps. Telephoto lenses or macro lenses may be employed based on the subject’s distance and detail requirements.
- Stabilization Tools: Tripods, gimbals, and steadicams are vital to maintaining smooth footage during high-speed recording. Their robustness ensures minimal camera shake, especially critical when capturing fast-paced scenes or performing dynamic movements.
Comparison of High Frame Rate Cameras
Different high frame rate cameras offer varied advantages and limitations, influencing their suitability based on specific project needs. Understanding these distinctions helps in selecting the most appropriate equipment for your desired outcomes.
| Camera Type | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Vision Research Phantom Series |
|
|
| Sony RX100 VII (Limited high fps) |
|
|
| Blackmagic URSA Mini Pro |
|
|
Accessories to Enhance High Frame Rate Recording
In addition to the primary equipment, several accessories significantly improve the quality and ease of high frame rate video production. These tools address specific challenges such as lighting, data handling, and stabilization, ensuring professional results.
- External Recorders: Devices like Atomos Ninja V or Blackmagic Video Assist extend recording capabilities, offload data from the camera, and provide higher bit-rate outputs for better image fidelity.
- Lighting Setups: High-intensity, flicker-free LED lights or continuous lighting systems are essential for maintaining proper exposure at high shutter speeds and fast frame rates, which typically demand more light than standard filming.
- High-Speed Memory Cards and Storage: Fast, reliable SSDs, CFast, or UHS-II SD cards with high write speeds prevent data bottlenecks during recording sessions that generate large volumes of footage.
- Gimbals and Rigs: Advanced stabilization rigs designed for high-speed cameras ensure steady footage even during rapid or complex movements, reducing jitter and vibrations that detract from professional quality.
Lighting Techniques for High Frame Rate Filming

Effective lighting is crucial when shooting high frame rate videos, as increased frame rates demand sharper, well-illuminated images to preserve clarity and detail. Proper lighting not only enhances image quality but also helps control exposure, prevent motion blur, and maintain the desired cinematic aesthetic. Achieving optimal lighting conditions is essential for capturing fast-moving subjects with precision and without compromise.
In high-speed filming, lighting conditions directly influence the ability to balance exposure and prevent motion artifacts such as motion blur. Since high frame rates require shorter shutter angles and faster shutter speeds, scenes often need more light to compensate for reduced exposure time per frame. Proper lighting setups and equipment choices can significantly improve image sharpness and overall video quality, ensuring that fast motion is crisp and visually appealing.
Lighting Conditions and Optimal Setups for High Frame Rate Shooting
Lighting conditions have a profound impact on high frame rate videos, as insufficient illumination can lead to underexposed images, increased noise, and loss of detail. Conversely, overly intense lighting can cause glare or overexposure, particularly in scenes with reflective surfaces or bright backgrounds. The key is to establish a balanced lighting environment that provides sufficient brightness without sacrificing image quality or creating unwanted shadows.
Optimal lighting setups for high frame rate filming involve the use of diffuse, evenly distributed light sources that minimize harsh shadows and highlight fast-moving subjects. High CRI (Color Rendering Index) lights are recommended to accurately reproduce colors, which is especially important when capturing intricate details or skin tones. Softboxes, diffusion panels, and LED panels with adjustable brightness and color temperature are preferred for their versatility and ability to create a consistent lighting environment.
Methods to Balance Exposure and Prevent Motion Blur in Fast Motion Scenes
Fast motion scenes require careful exposure management to ensure clarity and reduce motion blur. Achieving proper balance involves adjusting shutter speed, ISO, and aperture settings simultaneously, as these parameters collectively influence exposure and image sharpness. Employing the 180-degree shutter rule — where shutter speed is set to approximately twice the frame rate — is a foundational guideline to maintain natural motion portrayal while avoiding excessive motion blur.
To prevent motion blur at high frame rates, increase the shutter speed proportionally. For instance, at 120 fps, a shutter speed of 1/240 second is recommended. However, higher shutter speeds reduce the amount of light reaching the sensor, necessitating additional lighting or wider apertures to maintain proper exposure. Using ND (Neutral Density) filters allows filmmakers to reduce incoming light without altering exposure settings, especially in bright environments, thereby facilitating the use of faster shutter speeds without overexposing the image.
Lighting Equipment Suitable for High-Speed Shooting
Choosing the right lighting equipment is vital for high-speed filming, as it ensures consistent illumination and color accuracy under demanding conditions. The ideal lights for high frame rate production should provide high brightness levels, adjustable color temperatures, and minimal flicker — which can cause strobing or banding in fast-moving footage.
| Lighting Equipment | Features and Specifications |
|---|---|
| High-CRI LED Panels | CRI 95+, adjustable brightness and color temperature (3200K-5600K), flicker-free operation for smooth, consistent lighting |
| Fresnel Lights | Focusable beam angles, high output, durable construction, often equipped with DMX control for precise adjustments |
| Softboxes and Diffusion Panels | Soft, uniform light dispersion, reduces harsh shadows, compatible with LED or tungsten fixtures |
| Flicker-Free Fluorescent or LED Lights | Designed specifically for high-speed filming to prevent flickering at high shutter speeds, often with adjustable flicker settings |
| Neutral Density (ND) Filters | Allow reduction of light entering the lens, enabling faster shutter speeds without overexposure, available in various densities |
Important: When selecting lighting for high frame rate filming, prioritize flicker-free capabilities and high color rendering to ensure the footage remains sharp and color-accurate even at elevated shutter speeds.
Recording Techniques and Procedures

Achieving high-quality high frame rate footage requires meticulous planning and precise execution of recording procedures. This involves careful setup of camera equipment, synchronization of settings with scene dynamics, and awareness of potential challenges that may arise during filming. Mastering these techniques ensures smooth recording sessions and optimal footage quality, enabling filmmakers and videographers to capture fast-moving actions with clarity and detail.
Implementing effective recording techniques involves a structured approach to setting up the camera environment, adjusting parameters to match scene requirements, and anticipating common pitfalls. This section provides a comprehensive guide to the step-by-step procedures necessary for successful high frame rate shooting, along with troubleshooting tips to address typical issues encountered during recording.
Step-by-step Procedures for Setting Up a High Frame Rate Shoot
Establishing a disciplined process ensures consistency and reliability during high frame rate recording sessions. Below are the essential steps to prepare your equipment and environment for capturing high-quality footage:
- Plan Your Scene and Determine Frame Rate: Analyze the scene’s motion complexity and decide on an appropriate high frame rate (e.g., 120 fps, 240 fps). For fast fast-moving objects or action sequences, higher frame rates provide smoother slow-motion playback.
- Choose Suitable Camera Settings: Set your camera to the desired high frame rate mode, ensuring it supports the selected rate without compromising resolution or bitrate.
- Configure Shutter Speed: Follow the “double the frame rate” rule; for example, at 120 fps, set shutter speed to approximately 1/240 second. This minimizes motion blur and preserves sharpness.
- Adjust ISO and Aperture: Balance exposure by fine-tuning ISO and aperture settings, especially since higher frame rates may require more light or wider apertures.
- Set Focus and Depth of Field: Use manual focus to prevent focus shifts during recording, and consider a smaller depth of field to emphasize motion clarity.
- Secure Camera Mounting: Use tripods, gimbals, or stabilizers to prevent unwanted movement, which becomes more noticeable at high frame rates.
- Conduct Test Shots: Record short test segments to verify settings, exposure, and focus, adjusting parameters as needed before the main shoot.
Synchronizing Camera Settings with Scene Requirements
Aligning camera configurations with the scene’s dynamics is crucial for capturing crisp, high-quality footage. Proper synchronization involves understanding the motion characteristics, lighting conditions, and desired playback effect:
- Match Shutter Speed to Scene Motion: For scenes with rapid movement, ensure shutter speed adheres to the rule of doubling the frame rate to maintain motion clarity. For slower scenes, slightly lower shutter speeds may be acceptable, but caution is needed to avoid motion artifacts.
- Adjust Frame Rate According to Scene Speed: Use higher frame rates for scenes with fast motion such as sports, action sequences, or fast-moving vehicles.
- Optimize Exposure Settings: Based on lighting conditions, adjust ISO, aperture, and ND filters to maintain proper exposure without introducing noise or motion blur.
- Balance Depth of Field and Focus: Select aperture values that provide sufficient depth of field to keep subjects in focus, especially when tracking fast-moving objects.
- Maintain Consistent Settings During Scene Changes: When transitioning to different scenes or lighting conditions, update camera settings accordingly to prevent inconsistencies in footage quality.
Common Pitfalls and Troubleshooting Tips During High Frame Rate Recording
High frame rate shooting presents unique challenges that can compromise footage quality if not addressed proactively. Recognizing potential issues and implementing troubleshooting strategies is essential for smooth recording sessions:
“Overexposure, motion artifacts, and focus drift are common problems that can be mitigated through proper planning and real-time adjustments.”
Below are frequent pitfalls and practical solutions:
- Overexposure or Underexposure: High frame rates reduce light per frame, leading to underexposed footage. Use ND filters to control light intake and ensure proper exposure levels.
- Insufficient Lighting: Fast shutter speeds demand more light; incorporate high-quality lighting to maintain brightness and clarity, especially in indoor or low-light environments.
- Camera Heat and Battery Drain: Extended high frame rate recording can cause overheating and rapid battery depletion. Use cooling accessories and extra batteries to sustain shooting sessions.
- Focus Loss During Motion: Rapid movement can cause focus to shift. Pre-focus manually on the subject and consider using autofocus with tracking features if available.
- Rolling Shutter Artifacts: Fast pans or quick movements may produce skewed or wobbly images. Use cameras with global shutter technology or stabilize the camera rig to minimize these effects.
- Synchronization Issues Between Multiple Cameras: When multi-camera setups are employed, synchronize frame rates, shutter speeds, and timecode to ensure seamless editing and playback.
Regularly reviewing test footage during production allows immediate identification of issues, enabling on-the-spot adjustments that save time and maintain footage integrity. Maintaining a checklist and documenting camera settings for each scene further streamlines the process and ensures consistency throughout the shoot.
Post-Production and Playback Tips
Effective post-production and thoughtful playback considerations are essential to maximize the quality and impact of high frame rate footage. These steps ensure that the cinematic potential of high frame rate videos is fully realized, whether for slow-motion effects, color accuracy, or seamless viewing experiences across different devices.
Processing high frame rate footage involves specialized techniques that can enhance visual appeal, emphasize motion, and ensure smooth playback. Proper editing, color grading, and stabilization are critical to maintaining the clarity and fluidity of high frame rate videos. Additionally, understanding how to correctly export and display this content on various devices ensures optimal viewing experiences for audiences across platforms.
Processing Techniques for High Frame Rate Footage
High frame rate videos often require specific processing approaches to bring out their full potential. One of the main advantages is the ability to create high-quality slow-motion effects without sacrificing image clarity. This involves exporting footage at a lower frame rate, such as 24fps or 30fps, from the original high frame rate files, resulting in smooth slow motion that retains detail and reduces motion blur.
Advanced interpolation algorithms can also be employed during post-production to generate intermediate frames, further enhancing slow-motion quality.
When working with high frame rate footage, it’s crucial to consider the intended playback speed and adjust the frame rate accordingly during editing. Software tools like Adobe Premiere Pro, DaVinci Resolve, or Final Cut Pro offer options to interpret footage and apply frame interpolation techniques, helping achieve the desired slow-motion effect while maintaining natural motion appearance.
Guidelines for Editing, Color Grading, and Stabilizing
Editing high frame rate videos involves maintaining the fluidity and sharpness inherent to the footage. For seamless editing, use high-performance systems capable of handling large file sizes and high data rates typical of high frame rate recordings. When color grading, leverage the high bit depth and dynamic range of high-resolution footage to enhance colors, contrast, and overall aesthetic. Proper color grading can also help mitigate any inconsistencies caused by different lighting conditions or camera settings during shooting.
Stabilization is particularly important in high frame rate footage, as any unwanted camera shake may be more noticeable due to the increased detail. Utilize stabilization tools within editing software to smooth out motion artifacts without sacrificing the sharpness of the footage. Applying gentle stabilization preserves the natural look while eliminating jarring movements that can distract viewers.
Exporting and Display Guidelines for High Frame Rate Content
Export settings play a vital role in preserving the quality of high frame rate videos. When exporting, select appropriate codecs and container formats, such as H.264 or H.265, that support high data throughput and efficient compression. Set the frame rate to match the final playback device or platform, typically 24fps, 30fps, or 60fps, depending on the desired effect and audience expectations.
For slow-motion content, export at a lower frame rate with corresponding playback speed adjustments.
Displaying high frame rate videos across various devices requires consideration of the hardware capabilities. Modern smartphones, high-end monitors, and 4K televisions are capable of rendering 60fps or higher smoothly. For platforms like YouTube or Vimeo, ensure the uploaded videos adhere to their recommended specifications to prevent unnecessary compression artifacts. When presenting high frame rate content in live settings, such as cinemas or large screens, verify that the playback systems support the native high frame rate to preserve the cinematic quality.
Note: Consistent frame rate and proper encoding are crucial to maintaining the high-quality motion and detail captured during filming, ensuring viewers experience the full benefits of high frame rate production.
Creative Applications of High Frame Rate Footage
High frame rate (HFR) video recording opens up a multitude of creative possibilities that significantly enhance visual storytelling. Its ability to capture intricate details and smooth motion offers filmmakers, content creators, and professionals in various fields innovative ways to engage audiences and convey complex ideas through dynamic imagery. Understanding the diverse applications of HFR footage allows for more strategic and impactful use in different scenarios, from artistic expression to scientific analysis.
Leveraging high frame rate footage enables creators to craft immersive experiences, clarify fast-paced actions, and reveal subtle nuances often missed by standard frame rates. This technology extends beyond traditional filmmaking, finding vital roles in sports, scientific research, and commercial productions, thereby broadening the creative horizon for visual professionals.
Slow-Motion Highlights and Artistic Effects
One of the most prominent uses of high frame rate footage is creating stunning slow-motion sequences that emphasize detail and emotion. For example, capturing a dancer’s intricate movement or a splash of water in ultra-slow motion allows viewers to observe every fluid motion, enhancing aesthetic appeal and emotional impact. High frame rates enable smooth, high-quality slow-motion that maintains clarity and sharpness even when slowed down significantly, often at 120 fps or higher.
Scientific Analysis and Precision Observation
High frame rate recording is invaluable in scientific fields requiring precise motion analysis. It allows researchers to study phenomena such as fluid dynamics, material deformation, or biological processes with exceptional clarity. For instance, high-speed cameras used in biomechanics can analyze the rapid motion of a sprinter’s muscles or a bird’s wing flutter, providing insights that are critical for scientific advancements and engineering innovations.
Sports Filming and Action Capture
In sports production, high frame rate footage captures fast-paced actions with unparalleled detail, enabling broadcasters and viewers to analyze techniques, improve performance, and create engaging highlight reels. For example, slow-motion replays of a gymnast’s flip or a soccer player’s kick showcase the precision of athletic movements, making the footage both educational and entertainment-enhancing.
Enhancing Storytelling and Viewer Engagement
The ability to depict motion with remarkable smoothness and clarity enhances storytelling by immersing viewers in dynamic scenes. High frame rate footage can intensify action sequences, dramatize slow-building tension, or highlight subtle gestures and expressions, thereby fostering a deeper emotional connection. This technique not only improves visual quality but also elevates narrative depth, making scenes more memorable and engaging for audiences.
Closure
By applying the principles and techniques Artikeld, you can produce stunning high frame rate videos that captivate audiences and serve various creative and professional purposes. From precise camera setups to effective lighting and post-processing, mastering high frame rate shooting equips you with the skills to take your videography to the next level. Embrace these practices to bring your dynamic visions to life with clarity and fluidity.