Efficiently organizing video files is essential for maintaining a streamlined digital workspace and ensuring quick access to your content. Implementing a structured approach not only saves time but also enhances productivity when handling large multimedia libraries.
This guide explores key principles such as creating hierarchical folder structures, adopting consistent naming conventions, utilizing metadata and tags, and leveraging media management software. Additionally, it covers best practices for backup routines and ongoing maintenance to keep your video collection well-organized and easily retrievable.
Creating an efficient folder hierarchy
Establishing a well-structured folder hierarchy is fundamental for managing video files efficiently. A logical and consistent directory structure not only simplifies locating specific videos but also streamlines the workflow for editing, reviewing, and archiving. Proper organization reduces the risk of misplaced files and enhances collaboration across teams or projects. Implementing a thoughtful hierarchy from the outset facilitates long-term management and scalability as your collection of video files grows.An effective folder hierarchy typically involves defining main directories for broad categories and subdividing these into specific subfolders based on project details, formats, or dates.
This systematic approach ensures that every video file is stored in a designated location aligned with its purpose. Consistency in naming conventions across the hierarchy further improves searchability and clarity. Maintaining clear, descriptive folder and file names helps prevent confusion and supports efficient retrieval, especially when dealing with large volumes of video content.
Establishing main folders and subfolders for different video categories
Creating a logical hierarchy begins with identifying the primary categories relevant to your video collection. These categories often include project names, content types, formats, or production stages. Main folders should be broad enough to encompass all related files but specific enough to avoid clutter. Subfolders can then be used to organize individual projects, dates, or formats, providing a layered structure that enhances navigability.When designing your folder hierarchy, consider the nature of your workflow.
For instance, a typical structure might involve a main folder named “Videos,” with subfolders such as “Projects,” “Raw Footage,” “Edited Videos,” and “Exports.” Within each, further subdivisions can be created—such as by project name or date—to facilitate quick access. Utilizing consistent naming conventions for these folders ensures clarity. For example, naming a project folder “ClientXYZ_Interview_2024” immediately conveys its content and context.
Organizing videos by project, date, or format using a table
Effective categorization can be achieved by organizing videos according to specific criteria such as project, date, or format. A tabular approach provides clarity on how each folder serves a particular purpose, along with examples for implementation.
| Folder Name | Purpose | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Project_Name | Contains all files related to a specific project, serving as the primary organizational level. | Wedding_2024, ProductLaunch_Q2 |
| Date | Organizes files based on the date of recording or editing, helpful for chronological tracking. | 2024_04_15, 2024_03_10 |
| Format | Separates files based on their format or resolution, aiding in quick access for processing or output. | Raw_Footage, Edited_Versions, Final_Exports |
Developing a systematic procedure for naming folders based on these categories enhances consistency. For example, combining project name and date—“ClientXYZ_Interview_2024_04_15”—provides comprehensive context at a glance. Such conventions should be documented and shared across teams to maintain uniformity, reducing errors and ensuring everyone can navigate the hierarchy with ease.
Consistency in naming and structuring folders is crucial for scalable, efficient video file management.
Utilizing Metadata and Tags

Effective management of video files extends beyond organization within folders. Applying appropriate metadata and tags significantly enhances searchability, retrieval speed, and overall workflow efficiency. Metadata provides contextual information about each file, making it easier to locate videos based on content, date, subject, or other criteria. Tags serve as s or descriptive labels that further streamline the classification process, especially in large media libraries or editing projects.
Properly leveraging metadata and tags ensures your video collection remains structured, accessible, and easy to navigate, saving valuable time during post-production or review processes.Metadata application involves embedding detailed information directly into the video file properties or associated databases. This data can include titles, descriptions, creators, dates, and copyright details, which are recognized by most media players and management software. Tags, on the other hand, are usually added as s or comments within the file’s metadata fields, offering flexible categorization based on themes, topics, or project-specific s.
Using consistent and descriptive metadata and tags allows for refined filtering, searching, and sorting, which is particularly beneficial when handling hundreds or thousands of video files. Moreover, well-structured metadata enhances compatibility with digital asset management systems, facilitating collaborative workflows and version control.
Applying Metadata to Video Files
Applying metadata correctly is crucial for maximizing the benefits of organized video libraries. Modern operating systems and media management tools provide options to edit file properties directly within the file system interface or through dedicated media management software. It is advisable to develop standardized templates for metadata entries to maintain consistency across various video projects and types.For example, a video intended for social media promotion might include metadata such as:
| Field | Example Content |
|---|---|
| Title | Summer Campaign 2024 Launch |
| Description | A promotional video showcasing the upcoming summer collection with vibrant visuals and testimonials. |
| Author/Creator | Jane Doe |
| Date Created | 2024-05-10 |
| s/Tags | Summer, Campaign, Promotion, Fashion, 2024 |
Similarly, a tutorial or educational video could have metadata such as:
“Educational content focusing on video editing techniques for beginners, suitable for YouTube tutorials or online courses.”
Title
Video Editing Basics for Beginners
Description
A step-by-step guide covering fundamental editing techniques using Adobe Premiere Pro.
s
Video editing, tutorials, beginner, Adobe Premiere, filmmakingTo add metadata, users can employ media management software like Adobe Bridge, VLC Media Player, or dedicated tagging tools such as MP3Tag or MetaX. For bulk editing, scripts or command-line tools like ExifTool can streamline the process, especially when dealing with large collections.
Adding Descriptive Tags, s, and Comments
Tags and descriptive s are vital for categorization and quick retrieval, especially in extensive video libraries or cloud-based storage solutions. These tags should be relevant, specific, and consistent to ensure effective filtering. When adding tags, consider the primary themes, subjects, or project details that will help distinguish one video from another.Adding comments or descriptive annotations within file properties is equally helpful for providing contextual information that may not be captured fully by tags alone.
Comments can include additional notes about the content, editing instructions, or licensing details, which are accessible through file property dialogs or management software.It is recommended to maintain a standardized tagging vocabulary, including common s such as location names, event types, or project phases, to facilitate cross-referencing across the library. Regular audits of metadata and tags can help identify inconsistencies or outdated information, maintaining the integrity and usability of your video archive.By systematically applying metadata and tags, video files become more than just stored data—they transform into a structured, searchable resource that supports efficient project management, content retrieval, and collaboration efforts.
Using Media Management Software
Efficient organization of video files can be significantly enhanced through the utilization of specialized media management software. These tools streamline the process of importing, categorizing, and retrieving video content, making large collections manageable and accessible. By adopting such software, users can save time, improve workflow, and ensure a structured digital library that supports various professional and personal projects.
Media management software offers a range of features designed to simplify video file handling. These include automatic metadata extraction, customizable tagging systems, batch processing capabilities, and advanced search functions. Such features enable users to quickly locate specific videos based on attributes like date, file type, tags, or content descriptions. The integration of these tools into everyday workflows results in a more organized, efficient, and scalable video library.
Features of Popular Video File Organizers and Their Benefits
Many media management applications are available today, each with unique features catering to different user needs. Here are some of the most widely used options, along with their core benefits:
- Adobe Bridge: Offers robust metadata management, batch editing, and seamless integration with Adobe Creative Cloud. Ideal for professional editors needing comprehensive control over large video archives.
- VLC Media Player: Primarily a media player, but includes features for organizing and creating playlists, along with basic tagging options. Suitable for casual users who need quick access and playback functionality.
- Shotcut: An open-source video editor with built-in organizational tools, including metadata editing and project management. Perfect for users seeking free yet functional organization capabilities.
- Adobe Lightroom (with video support): Known for photo management, it also supports video tagging and metadata editing, facilitating integrated media workflows for multi-format creators.
- Plex Media Server: Designed for home media libraries, it automatically catalogs videos, fetches metadata from online databases, and provides an intuitive interface for browsing and streaming content across devices.
These tools enhance productivity by automating routine tasks, providing detailed metadata options, and enabling efficient categorization, which simplifies future retrieval of specific video files.
Importing, Categorizing, and Searching Videos
Effective media management software includes straightforward methods for importing videos, assigning categories, and conducting searches, which are crucial for maintaining an organized collection. Users should leverage these functionalities to optimize their workflow:
- Importing Videos: Most software allows drag-and-drop importing or batch processing to handle multiple files simultaneously. During import, users can assign initial metadata or tags to facilitate sorting and searching later.
- Classifying and Categorizing: Use predefined categories such as genre, project, date, or custom tags to classify videos systematically. Many applications enable creating smart collections or filters that automatically update as new videos are added, maintaining consistency across the library.
- Searching for Videos: Advanced search features include filtering by metadata, tags, or content descriptions. Some programs incorporate AI-based content recognition, allowing users to search videos based on visual or audio cues, further enhancing ease of access.
Utilize metadata and tagging consistently during import to create a searchable, well-structured library. Regularly updating and maintaining these attributes ensures that files are easily retrievable even after extensive collection growth.
By efficiently importing, categorizing, and searching videos within media management software, users can dramatically reduce time spent locating specific files, which in turn enhances overall productivity and organization quality.
Comparison Table of Video Management Software Options
This table summarizes the key features, supported platforms, and pricing models of popular video file organizers, aiding users in selecting the best tool for their needs:
| Software | Features | Platforms | Pricing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adobe Bridge | Metadata management, batch editing, integration with Adobe CC | Windows, macOS | Free |
| VLC Media Player | Media playback, playlist creation, basic organization | Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, Android | Free |
| Shotcut | Open-source editing, metadata support, organizational tools | Windows, macOS, Linux | Free |
| Plex Media Server | Automatic metadata fetching, streaming, library management | Windows, macOS, Linux, NAS devices, mobile apps | Free basic, Premium plans start at $4.99/month |
| Adobe Premiere Pro | Professional editing, metadata, categorization, search features | Windows, macOS | Subscription-based, approx. $20.99/month |
Selection depends on specific needs, budget, and platform compatibility. For casual users, free tools like VLC or Shotcut may suffice, while professionals may prefer Adobe solutions or Plex for comprehensive management and streaming capabilities.
Backup and Version Control
Effective management of video files extends beyond organization and editing workflows to include reliable backup and version control measures. Implementing robust procedures for safeguarding your organized video library ensures data integrity, minimizes the risk of data loss, and streamlines collaborative editing processes. Maintaining multiple versions of editing projects allows for easy reversion to previous stages, facilitates comparison of edits, and supports iterative creative workflows.
By establishing clear backup routines and versioning strategies, content creators and editors can operate with confidence, knowing their valuable footage and projects are protected and manageable.
Procedures for Secure Backup of Organized Video Libraries
Reliable backup procedures are critical for preventing data loss caused by hardware failures, accidental deletions, or cyber incidents. These procedures involve creating copies of your entire video library at regular intervals and storing them in secure, off-site locations. Implementing multiple backup layers ensures redundancy, while encryption enhances data security during transfer and storage. It is essential to verify backups periodically to confirm their integrity and to document backup schedules and procedures for consistency.
Key steps in securing video library backups include:
- Scheduling regular backups aligned with project updates or new footage acquisition.
- Using encryption protocols such as AES-256 to secure stored backups against unauthorized access.
- Storing backups in geographically separated locations, such as cloud services and physical drives, to mitigate risks of physical damage or theft.
- Maintaining detailed logs of backup dates, contents, and storage locations for audit and recovery purposes.
Reliable backup solutions may involve cloud storage providers like Amazon S3, Google Drive, or specialized backup services tailored for media content. External hard drives or NAS devices configured with RAID can serve as local backup repositories, ensuring quick recovery and access when needed.
Strategies for Maintaining Multiple Project Versions
Managing multiple versions of editing projects allows editors to preserve progress at various stages, compare different edits, and revert to earlier versions if necessary. Effective version control reduces the risk of overwriting important edits and enhances collaborative workflows by providing a clear history of changes.
Implementing a systematic approach to versioning involves:
- Adopting a consistent naming convention that includes version numbers, dates, and brief descriptions (e.g., “ProjectName_v01_20241015”).
- Saving incremental versions periodically during editing sessions, especially before significant changes.
- Using dedicated version control folders within the project directory, such as a “Versions” folder, to organize different project iterations.
- Employing media management software that supports automatic version saving or snapshot features, reducing manual effort.
“Maintaining clear and structured project versions facilitates seamless collaboration and minimizes loss of creative work.”
For complex projects involving multiple editors or team members, utilizing revision control tools or cloud-based collaboration platforms like Adobe Creative Cloud or Frame.io can streamline version management, ensuring everyone accesses the latest project state while preserving historical edits.
Implementing Automated Backup Routines with Storage Options
Automation of backup routines ensures consistency and minimizes manual intervention, thereby reducing the likelihood of data loss. Establishing automated routines involves configuring backup software or scripting solutions to perform scheduled backups to designated storage locations, with predefined parameters for frequency and scope.
Recommended backup options and storage locations include:
| Backup Option | Storage Location | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud Backup | Amazon S3, Google Drive, Dropbox | Remote accessibility, scalability, disaster recovery |
| External Hard Drives | Physical drives connected via USB or Thunderbolt | Fast local access, cost-effective for large files |
| Network Attached Storage (NAS) | On-premises networked storage devices | Centralized management, multiple backups, redundancy |
| Automated Backup Software | Configured to run on schedules using tools like Acronis, Macrium, or custom scripts | Consistency, minimal manual effort, customizable routines |
Sample steps to set up an automated backup routine:
- Select backup software compatible with your operating system and storage options.
- Define backup schedules—daily, weekly, or after each editing session, depending on project criticality.
- Configure backup scope, selecting entire video libraries, project files, and metadata folders.
- Set up notifications for backup success or failure to promptly address issues.
- Regularly review and update backup configurations to accommodate evolving project needs.
Tips for ongoing maintenance
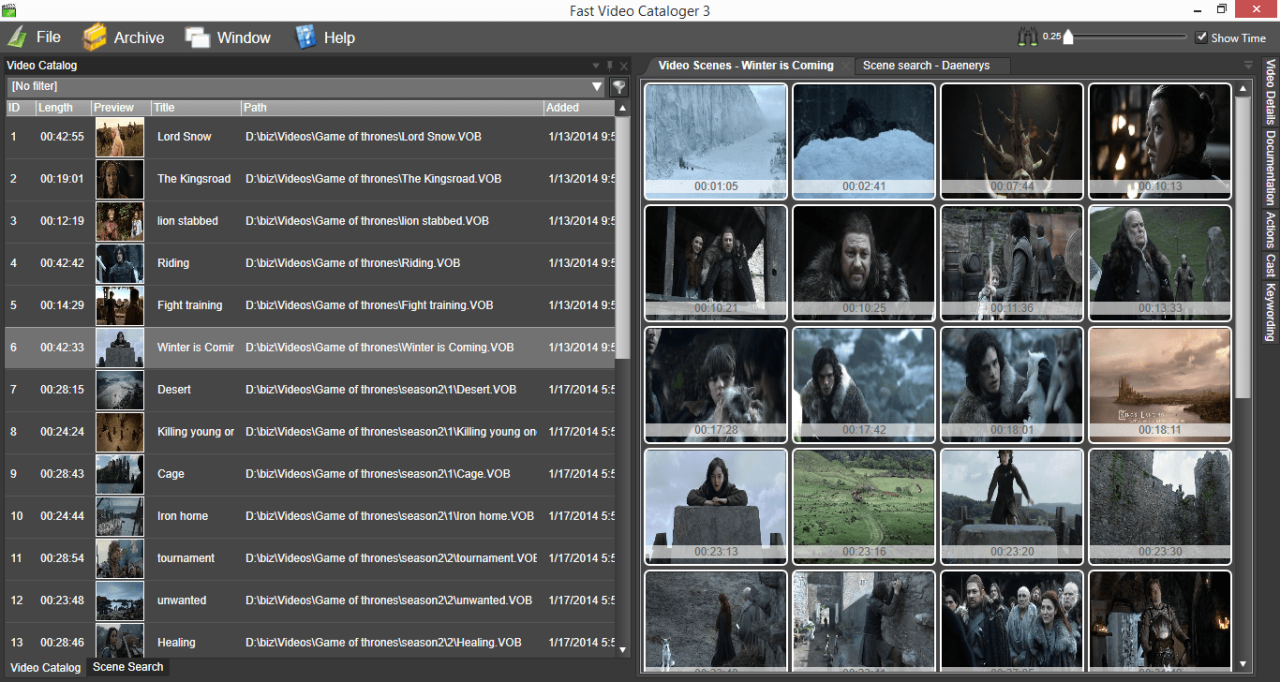
Maintaining an organized video library is an ongoing process that ensures your files remain accessible, accurate, and manageable over time. Regular upkeep not only prevents clutter but also enhances productivity, especially as your collection grows. Implementing routine checks and updates can save considerable time and effort in the long run, ensuring your video assets are always ready for use whenever needed.Consistent maintenance involves scheduling periodic review sessions to tidy, update, and optimize your video files.
Systematic archiving of completed or outdated projects helps keep your active workspace streamlined and focused. Additionally, documenting your organizational workflows and protocols guarantees that your system remains coherent and can be easily understood or recreated by others or yourself in the future. These practices sustain the integrity of your media management system and support ongoing project efficiency.
Regular tidying and updating routines
Incorporating routine tidying into your media management process is essential to prevent accumulation of redundant or obsolete files, which can hamper workflow. Establishing a schedule—such as monthly or quarterly reviews—ensures consistent upkeep. During these reviews, assess your current folder structures, delete duplicate or unused files, and verify that file naming conventions remain clear and consistent. Updating metadata and tags during these sessions guarantees that searchability and categorization stay accurate, facilitating swift access to relevant videos.An effective routine also involves monitoring storage health and capacity.
Moving older, less frequently accessed files to secondary drives or cloud storage reduces clutter in primary working directories. Implementing a checklist for each review session can help maintain discipline and completeness, ensuring nothing is overlooked.
Systematic archiving of old projects
Archiving is a critical component of ongoing media management, enabling the preservation of completed projects while keeping active folders uncluttered. Systematic archiving involves categorizing projects based on completion date, project type, or relevance, then moving them into designated archival locations. Use clearly labeled folders or storage media, such as external drives or cloud archives, to facilitate future retrieval when needed.An effective approach includes creating an archive index or catalog that records key details of each project, such as project name, date, involved personnel, and storage location.
This index acts as a quick reference, reducing time spent searching for archived files. Additionally, periodically reviewing archived content ensures outdated or irrelevant projects are either reclassified or removed, maintaining an efficient archive system.
Documenting organizational workflows for future reference
Maintaining comprehensive documentation of your media management system is invaluable for ensuring consistency and ease of onboarding new team members or revisiting your workflow after an extended period. Record your folder hierarchies, naming conventions, tagging strategies, and software usage protocols in a clear, accessible format.Creating detailed workflow guides or manuals helps preserve institutional knowledge, especially when updates or changes are made to the system.
These documents should include step-by-step procedures for routine maintenance, archiving, and metadata management. Regularly updating this documentation keeps it current, providing a reliable foundation for ongoing organizational excellence and quick onboarding for new personnel.
Troubleshooting Common Organization Issues

Organizing extensive video collections can sometimes present unexpected challenges that disrupt workflow and accessibility. Addressing these issues promptly ensures that your media management remains seamless and efficient. Understanding common problems and their solutions helps maintain the integrity and usability of your video library, preventing frustration and potential data loss.Effective troubleshooting involves identifying frequent issues such as broken links, misplaced files, and inconsistent naming conventions.
Recognizing these problems early and applying targeted solutions can significantly improve your organizational system, saving time and reducing errors. The following discussion offers practical guidance on resolving typical issues encountered during video file management.
Identifying and Resolving Broken Links
Broken links typically occur when video files are moved, renamed, or deleted without updating the associated references within media management software or catalogs. These disruptions can hinder access to important files, especially in large collections spanning multiple storage locations.To troubleshoot broken links:
- Verify the file path: Confirm whether the file still exists in its original location or has been relocated. Use your operating system’s search function to locate missing files.
- Update file references: In media management software or catalogs, re-link the files by pointing to their new location. Most programs offer a “relink” or “update link” feature for this purpose.
- Restore deleted files: If files were unintentionally deleted, check the recycle bin or backup copies to recover them.
Maintaining a consistent folder hierarchy and avoiding frequent file movements without updating links are critical preventive strategies.
Addressing Misplaced Files and Inconsistent Naming
Misplaced files and inconsistent naming conventions are common issues that complicate file retrieval and organization. Files stored outside designated folders or named arbitrarily can cause confusion and inefficiency.To resolve these issues:
- Conduct an audit: Regularly review your collection to identify files that do not adhere to your organized structure or naming standards.
- Implement standardized naming conventions: Use descriptive, consistent filenames that include relevant metadata such as date, project name, or sequence number.
- Relocate misplaced files: Move files to their correct folders based on your established hierarchy, ensuring that folder structures align with your naming scheme.
- Automate renaming: Utilize batch renaming tools or scripts to correct naming inconsistencies efficiently across multiple files.
Adopting strict naming protocols and periodic audits will minimize misplacement and inconsistency issues over time.
Troubleshooting Checklist Table
The following table offers a quick reference guide for diagnosing and resolving common video organization problems:
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Broken links or missing files | File moved, renamed, or deleted without updating references | Locate files, update links in software, or restore from backup |
| Files stored outside designated folders | Misplacement during file transfer or lack of folder discipline | Reorganize files into the correct structure and enforce folder policies |
| Inconsistent or unclear filenames | Lack of standardized naming conventions | Implement naming standards and batch rename affected files |
| Duplicate files or versions | Multiple copies created inadvertently | Identify duplicates, consolidate or delete redundant files |
| Metadata loss or errors | Incorrect tagging or file corruption | Reapply correct metadata, verify file integrity, and update tags accordingly |
Using this troubleshooting table as a quick diagnostic reference can facilitate rapid problem resolution, ensuring your video collection remains organized and accessible.
Final Summary
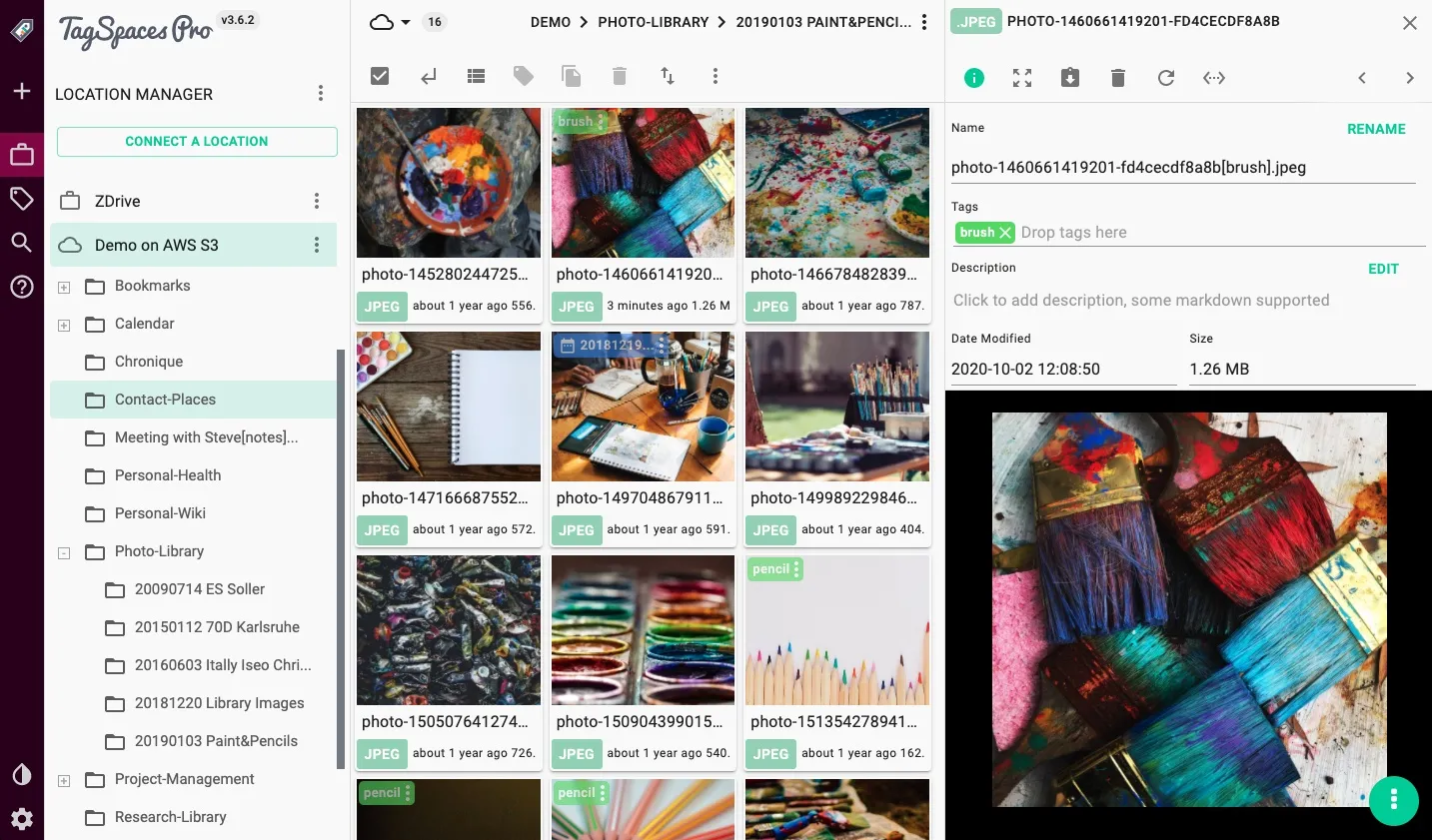
Mastering the art of organizing video files empowers you to manage your multimedia assets effectively, reducing clutter and improving workflow efficiency. With systematic strategies in place, maintaining a tidy and accessible video library becomes a manageable and rewarding task, ensuring your content is always ready when needed.