Learning how to add transitions is essential for creating smooth and engaging digital content across various platforms. Whether you’re working with videos, web pages, or presentations, incorporating effective transitions can significantly enhance the viewer’s experience by providing fluid visual shifts and maintaining audience interest.
This guide explores different types of transitions, methods for implementing them, and best practices to ensure your content looks professional and cohesive. From CSS techniques to presentation software steps, you’ll discover practical tips to elevate your multimedia projects seamlessly.
Overview of Adding Transitions in Digital Content
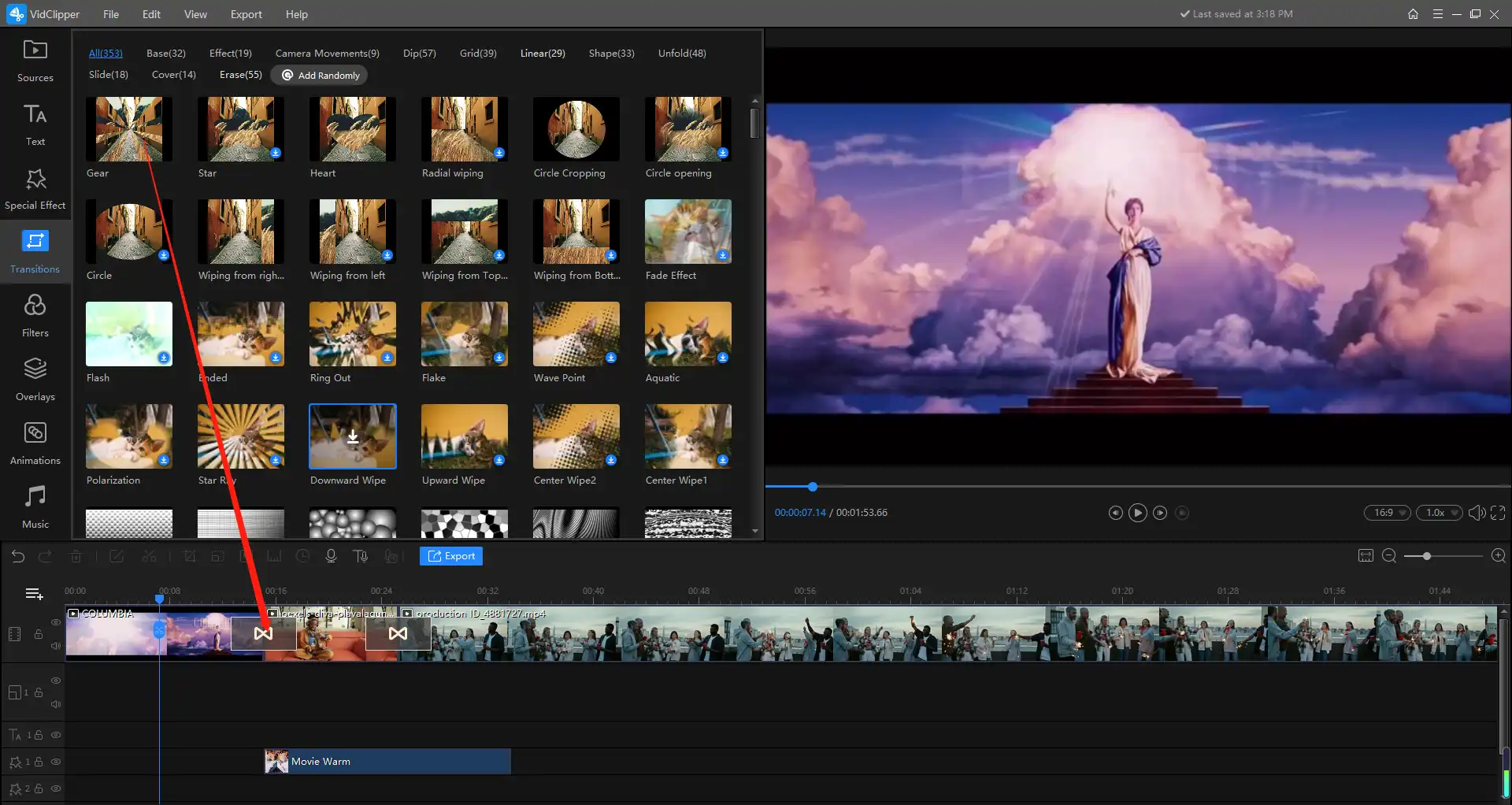
In the realm of digital content creation, transitions serve as essential tools that facilitate seamless movement between different elements, scenes, or sections. They play a vital role in enhancing the visual narrative by providing smooth and professional shifts that capture the viewer’s attention and maintain engagement. Properly integrated transitions can transform an ordinary presentation or multimedia project into a polished and compelling experience, making the content more appealing and easier to follow.
Transitions are widely utilized across various digital platforms, including video editing, website design, and multimedia presentations. They help bridge gaps between scenes, slides, or segments, ensuring continuity and coherence. The strategic use of transitions can significantly impact user experience by guiding viewers naturally through the content, emphasizing key points, or creating dramatic effects when necessary. Different types of transitions cater to specific needs, from subtle fades for a gentle flow to dynamic slides and wipes for energetic shifts, each contributing uniquely to the overall aesthetic and functionality of digital content.
Types of Transitions in Multimedia and Web Design
The diversity of transitions available today allows content creators to tailor their visual storytelling to suit the tone and purpose of their project. Understanding the various types of transitions enhances the ability to select appropriate effects that complement the content and audience expectations.
| Transition Type | Description | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Fade | A gradual change where one scene or element slowly appears or disappears, creating a smooth transition. | Used to suggest a passage of time, emotional shifts, or to soften scene changes in videos and presentations. |
| Slide | Shifts the current scene or slide off-screen while bringing in the next from a specified direction. | Common in slideshows and web interfaces to indicate a movement or progression between sections. |
| Wipe | Replaces one scene with another through a moving line or shape, effectively “wiping” the previous content away. | Often used in video editing for stylistic effects or in web design to transition between pages. |
| Zoom | Magnifies or reduces the view, creating a dynamic transition that draws attention to specific details or shifts focus. | Effective in tutorials, product showcases, or storytelling that benefits from a focus shift. |
| Flip | Creates a flipping motion, turning one scene over to reveal the next, similar to turning a page. | Popular in interactive interfaces and animated presentations for a modern, engaging look. |
“Choosing the appropriate transition depends on the context, desired emotional impact, and the overall aesthetic of the project.”
By understanding and leveraging these transition types, content creators can craft visually appealing sequences that enhance storytelling, improve clarity, and maintain viewer interest. Each transition type offers unique advantages that can be combined creatively to produce professional and engaging digital content across various mediums.
Types of Transitions and Their Effects
Understanding the various transition effects available in digital content creation is essential for producing engaging and professional presentations, videos, and slideshows. Each transition type can evoke different emotional responses and serve specific narrative purposes, making it crucial to select effects that complement the content’s tone and message.
Different transition effects offer unique visual styles and can significantly influence how viewers perceive the flow of information. Choosing appropriate transitions enhances viewer engagement, maintains the flow’s coherence, and emphasizes particular segments of your content.
Common Transition Effects and Their Applications
Below is a detailed overview of popular transition effects, including their descriptions and ideal use cases. Organizing these options into a structured format helps in selecting the best transition for each content type to achieve a seamless viewing experience.
| Effect | Description | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Fade | A gradual transition where one scene or slide smoothly dissolves into the next, creating a soft and subtle change. | Best suited for transitions between scenes with similar tones, such as moving from an introduction to a conclusion, or between slides in a presentation to maintain a calm and professional flow. |
| Slide | The new scene or slide slides in from a specified direction (left, right, up, or down), replacing the previous view with motion. | Effective for dynamic storytelling or emphasizing a change in topics, such as shifting from one section of a presentation to another, or showcasing before-and-after comparisons. |
| Wipe | A transition where a line or shape moves across the screen, revealing the next scene as it passes. | Ideal for artistic or creative projects, including promotional videos or presentations that require a stylized transition, or when introducing new segments with visual flair. |
| Zoom | The view gradually zooms in or out, focusing tightly on an element or revealing more of the scene. | Useful for emphasizing details, such as highlighting specific data points, or transitioning into close-up shots in video content. |
| Transition Effect Options | ||
| Fade | A smooth blend from one scene to another, creating a gentle transition that minimizes visual disruption. | Suitable for background music or narration changes, or transitioning between scenes with similar lighting and color schemes. |
| Slide | Scene or slide enters from one side, pushing the previous scene out, often with directional control. | Effective for segment shifts, such as moving from an overview into detailed content or showcasing step-by-step processes. |
| Wipe | A visual line or shape passes across the screen to reveal the next scene, which can take various forms like circular, diagonal, or custom shapes. | Great for creative presentations or to signal a change in topics with a visual cue, enhancing viewer engagement. |
| Zoom | The transition involves zooming in or out, creating a sense of focus or expansion. | Ideal for emphasizing specific content or actions, such as zooming into a chart or zooming out to show context in a video narrative. |
Methods for Adding Transitions in Video and Animation Software
In modern digital content creation, seamlessly connecting scenes or elements enhances viewer engagement and storytelling. Incorporating transitions between clips or animations requires familiarity with the tools and techniques available in popular editing software. Mastering these methods ensures smooth flow and professional quality in your projects, whether you’re editing a short video, a presentation, or an animated sequence.
Different video and animation programs offer a variety of options for inserting and customizing transitions. Understanding how to access these features, apply them effectively, and fine-tune their properties is essential for achieving the desired visual impact. Below, we Artikel step-by-step procedures and practical tips to help you efficiently add transitions across widely used editing platforms.
Inserting Transitions in Popular Editing Tools
Each editing software has its unique interface and workflow for adding transitions. Here are detailed procedures for some of the most common tools:
- Adobe Premiere Pro:
- Import your video clips into the project panel and drag them onto the timeline in sequential order.
- Navigate to the Effects panel and locate the Video Transitions folder.
- Browse through transition categories such as Dissolve, Wipe, or Slide.
- Drag the desired transition effect directly onto the cut point between two clips on the timeline.
- Adjust the transition length by dragging its edges on the timeline to refine the duration.
- Final Cut Pro:
- Arrange your clips on the timeline in the desired sequence.
- In the Transitions Browser, select a transition style suitable for your project.
- Drag the selected transition onto the junction between two clips or elements.
- Use the inspector panel to customize attributes such as duration, direction, or style.
- DaVinci Resolve:
- Import media and place clips on the timeline.
- Open the Effects Library and locate Transitions.
- Drag and drop a transition onto the cut between two clips.
- Click on the transition to access the inspector, where you can modify parameters like duration, alignment, and style.
Customizing Transition Duration and Style
Once a transition is inserted, tailoring its appearance and timing can significantly impact the overall flow of your project. Here are effective methods to customize transition properties:
- Adjust Transition Length:
- Drag the edges of the transition effect on the timeline to extend or shorten its duration.
- Set precise duration values in the properties or inspector panel for consistency across multiple transitions.
- Select Transition Style:
- Choose from predefined transition effects such as fades, wipes, zooms, or slides, depending on the software’s library.
- Apply different styles to emphasize mood or match the aesthetic of your content.
- Modify Transition Parameters:
- Access settings such as direction, color, or intensity within the transition properties.
- Experiment with different configurations to achieve desired visual effects.
- Use Keyframes for Advanced Customization:
- Implement keyframes to animate transition properties over time, creating dynamic effects.
- This allows for more precise control, especially in complex animations or sequences.
Previewing and Adjusting Transitions for Optimal Flow
Previewing your transitions ensures they integrate seamlessly into your project, maintaining a natural and engaging flow. Here are key practices:
- Play the Transition Segment:
- Use the software’s playback controls to review the transition in real-time.
- Observe how the transition complements the preceding and following clips or scenes.
- Refine Duration and Style:
- If the transition feels abrupt or sluggish, adjust its length or style accordingly.
- Iterate the preview process after each modification to gauge improvements.
- Utilize Frame-by-Frame Previewing:
- Use frame-by-frame controls for precise adjustments, especially in complex sequences.
- This approach helps identify the optimal moment to start or end a transition for perfect timing.
- Apply Real-Time Feedback Tools:
- Leverage software features like waveform monitors or color grading scopes to ensure visual consistency.
- Gather feedback from peers or clients by exporting short samples for review.
Implementing Transitions in Web Pages Using CSS and HTML

In modern web development, CSS transitions enable smooth and visually appealing effects when changing the properties of HTML elements. Implementing these transitions enhances user experience by providing fluid interactions, making web pages feel more dynamic and engaging. Properly applying CSS transitions requires understanding the syntax, the properties involved, and how to control the timing and easing functions for optimal results.
This section explores practical methods for incorporating transitions into web pages, comparing different CSS transition properties, and establishing best practices for timing and layering effects to create seamless animations and interactions.
Applying CSS Transitions Between Elements
CSS transitions are defined using the transition property, which specifies the properties to animate, the duration, easing function, and delay if necessary. The transition is typically triggered by changing a property value, such as on hover or focus states, enabling animated transformations or style changes.
Below is a simple example demonstrating how to add a transition effect to a button element that changes background color and scale on hover:
button
background-color: #4CAF50;
color: white;
padding: 12px 24px;
border: none;
cursor: pointer;
transition: background-color 0.3s ease-in-out, transform 0.2s ease;
button:hover
background-color: #45a049;
transform: scale(1.1);
In this example, when the user hovers over the button, the background color transitions smoothly over 0.3 seconds with an ease-in-out timing function, while the button scales up slightly within 0.2 seconds using an ease function. This creates a responsive and appealing visual feedback.
Comparative Overview of CSS Transition Properties and Effects
Understanding the different transition properties allows web developers to craft nuanced and sophisticated animations. The following table illustrates key CSS transition properties, their descriptions, and typical use cases:
| Property | Description | Example Usage |
|---|---|---|
transition-property |
Specifies one or more CSS properties to animate. Use * to target all animatable properties. |
transition-property: background-color, transform; |
transition-duration |
Defines the length of time the transition takes to complete, typically in seconds (s) or milliseconds (ms). |
transition-duration: 0.5s; |
transition-timing-function |
Controls the acceleration curve of the transition, affecting its pacing and feel. | ease-in-out, linear, ease-in, ease-out |
transition-delay |
Sets a delay before the transition begins, useful for sequencing multiple effects. | delay: 0.2s; |
Note: Combining multiple transition properties in a shorthand syntax simplifies code, e.g.,
transition: background-color 0.3s ease-in, transform 0.2s ease;
By selecting appropriate properties and timing functions, designers can create layered and intricate effects that enhance interactivity without overwhelming users. For example, layering a color change with a scale transformation can produce a compelling hover effect that feels both natural and engaging.
Best Practices for Timing, Easing Functions, and Layering Transitions
Effective use of transitions on web pages hinges on understanding how timing and easing influence user perception. Here are essential best practices:
- Consistent Timing: Use uniform durations for related transitions to maintain a cohesive visual flow, especially when multiple elements animate simultaneously.
- Easing Functions: Choose easing functions that match the context—
ease-in-outfor gentle starts and ends,linearfor uniform motion, or custom cubic-bezier curves for personalized effects. - Layering Transitions: Sequence multiple transitions using delays or staggered timing to guide user attention. For instance, fade in a modal then slide it into view with different timing settings to create a smooth entrance.
- Performance Optimization: Limit the use of box-shadow, filter, or other costly properties within transitions to prevent performance issues, especially on mobile devices.
- Accessibility Considerations: Avoid overly rapid or long transitions that may hinder users with cognitive or motor impairments. Providing an option to reduce motion via prefers-reduced-motion media queries enhances inclusivity.
Layering transitions thoughtfully can produce sophisticated effects that improve user engagement. For example, combining opacity and transform with different timing functions and delays can create a sense of depth and interactivity, making the webpage feel more alive and responsive.
Adding Transitions in Presentation Software
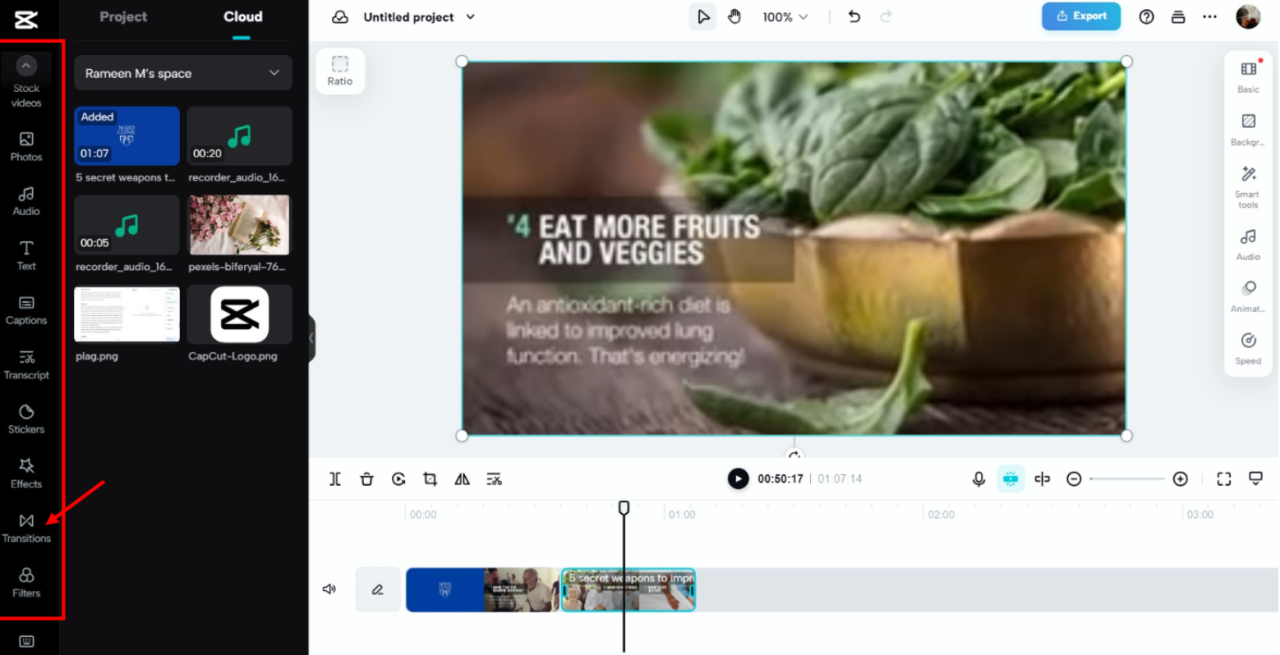
Transitions in presentation software play a vital role in creating smooth and engaging slide shows. They help in maintaining audience interest by adding visual dynamics between slides, making the presentation more professional and cohesive. Mastering the process of inserting and customizing transitions enhances the overall effectiveness of your presentation.
Whether using PowerPoint or Google Slides, understanding the procedures for applying transitions efficiently allows presenters to save time and ensure consistency throughout the presentation. Proper selection of transition effects can also reinforce the tone of the content, whether formal, creative, or casual, contributing to clearer communication and audience engagement.
Procedures for Inserting Transitions in PowerPoint and Google Slides
Inserting transitions involves selecting the desired effect and applying it to one or multiple slides within the presentation. Both PowerPoint and Google Slides provide user-friendly interfaces for this purpose, enabling quick customization and preview of effects.
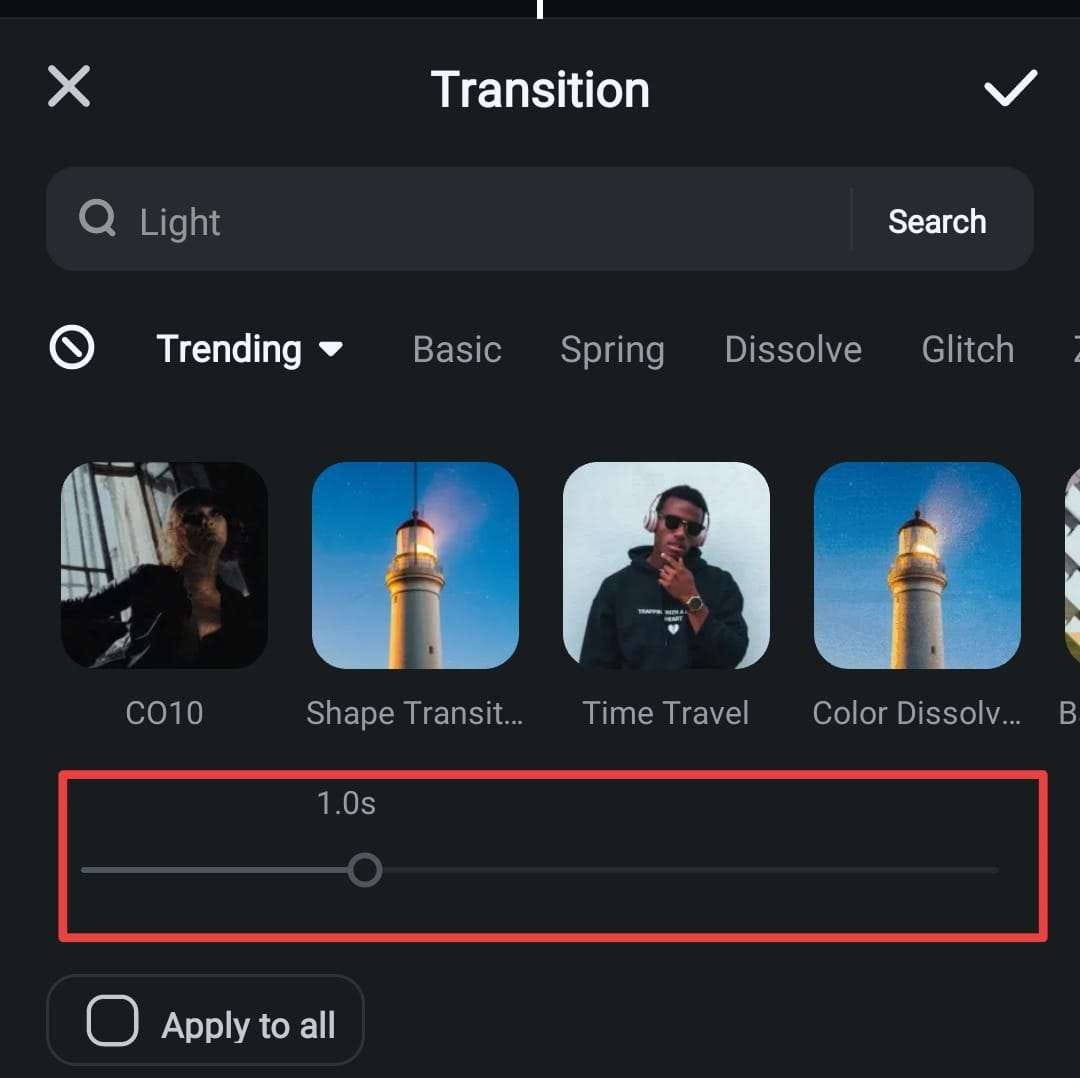
- PowerPoint: Open your presentation and navigate to the slide you wish to add a transition to. Click on the Transitions tab in the ribbon. Choose from the available transition effects such as Fade, Push, Wipe, or Morph. After selecting an effect, customize the duration and direction if applicable. To apply the same transition to multiple slides, select the slides in the slide pane, then click Apply To All or choose specific slides for individual transitions.
- Google Slides: Open your presentation and select the slide to modify. Click on the Transition button located in the toolbar. A sidebar will appear with transition options. Select your preferred effect from the dropdown menu, such as Dissolve, Slide, or Cube. Adjust the speed as needed.
To efficiently apply transitions to multiple slides, select the slides in the slide pane (using Shift or Ctrl/Cmd for multiple selections), then click Apply to all slides within the transition sidebar.
Tips for Selecting Transition Effects to Match Presentation Tone
Choosing the right transition effect is crucial for aligning the visual flow with the presentation’s purpose and tone. Subtle effects tend to suit formal or professional presentations, while more dynamic or creative transitions can enhance informal or innovative topics.
Consider the following guidelines when selecting transitions:
Match the Transition to Content and Audience: Use simple fades or wipes for serious or business presentations. For creative projects or storytelling, explore more vibrant effects like Flip or Morph. Avoid overly flashy effects that may distract or appear unprofessional.
Additionally, ensure consistency by limiting the number of different transitions used throughout the presentation. Repeatedly switching between complex effects can disrupt the visual harmony, whereas a consistent, minimal approach maintains a polished appearance.
Methods for Applying Transitions to Multiple Slides or Objects Efficiently
Applying transitions individually to each slide can be time-consuming, especially in large presentations. Efficient methods involve selecting multiple slides or using bulk application features within the software.
- Using Slide Master in PowerPoint: Customize transitions at the master slide level to automatically apply to all slides derived from that master. This approach ensures uniformity and saves time when dealing with extensive presentations.
- Applying to Multiple Slides: In PowerPoint, select multiple slides in the slide thumbnail pane by holding down the Shift or Ctrl/Cmd key. Then, choose the transition effect once, and it will be applied to all selected slides simultaneously. In Google Slides, select multiple slides similarly and then choose your transition, which applies to all selected slides in one action.
- Copy and Paste Transition Effects: In PowerPoint, you can copy a slide with the desired transition effect and paste it as a new slide, which retains the transition settings. This approach is useful for maintaining consistency when creating sections within a presentation.
Incorporating these methods not only streamlines the workflow but also ensures a consistent visual experience, enhancing the overall professionalism of the presentation.
Creating Seamless Transitions with JavaScript
Integrating JavaScript into transition effects enhances the interactivity and dynamism of digital content. By utilizing scripting techniques, developers can trigger transitions in response to user actions, creating a more engaging experience. Combining JavaScript with CSS allows for sophisticated transition sequences that can adapt seamlessly to various interactions, making web pages and applications more visually appealing and intuitive.
This section explores scripting methods to activate transitions dynamically, demonstrates how to blend JavaScript with CSS for advanced effects, and provides practical code examples illustrating transition sequences initiated through user interactions.
Scripting Techniques to Trigger Transitions Dynamically
Effective transition management begins with scripting strategies that respond to user inputs such as clicks, hovers, or scrolls. JavaScript provides event listeners and manipulation of style properties to initiate transitions on demand. Key techniques include:
- Event Listeners: Attaching listeners to DOM elements to detect interactions and trigger transition functions.
- Class Manipulation: Adding or removing CSS classes that contain transition-related styles, enabling smooth state changes.
- Inline Style Changes: Modifying element style properties directly through JavaScript to animate specific attributes like opacity, transform, or position.
These methods allow developers to craft responsive interfaces where transitions happen naturally in response to user behavior, enhancing usability and aesthetic appeal.
Combining JavaScript with CSS for Advanced Transition Effects
The synergy between JavaScript and CSS unlocks complex and highly customizable transition effects. JavaScript can dynamically modify CSS variables, trigger CSS animations, or manipulate inline styles to produce nuanced visual changes. This combination facilitates:
- Sequential Transitions: Sequencing multiple transition effects to create smooth, multi-stage animations.
- Conditional Effects: Applying different transition styles based on user input or application state.
- Responsive Animations: Adjusting transition parameters in real-time for device-specific or interaction-specific effects.
For instance, a JavaScript function can toggle classes that define transition durations, delays, and easing functions, resulting in highly flexible transition behaviors aligned with user actions.
Code Examples of Transition Sequences Activated by User Interactions
Below are practical code snippets illustrating how user interactions can trigger transition sequences using JavaScript, demonstrating real-time, seamless visual effects.
/* CSS: Define transition styles -/ .box width: 200px; height: 200px; background-color: #3498db; transition: all 0.5s ease-in-out; .box.expanded width: 400px; height: 400px; background-color: #e74c3c;
// JavaScript: Trigger transition on button click
const box = document.querySelector('.box');
const button = document.querySelector('#toggleButton');
button.addEventListener('click', () =>
box.classList.toggle('expanded');
);
In this example, clicking the button toggles the ‘expanded’ class on the box element, initiating a transition that smoothly enlarges the box and changes its color. Similar techniques can be employed to animate opacity, position, or other CSS properties, creating engaging, responsive transition effects synced with user interactions.
Best Practices and Tips for Effective Transitions
Implementing transitions effectively enhances the visual flow of digital content, making it more engaging and seamless for viewers. Selecting appropriate transition types and applying them thoughtfully ensures that the transitions serve their purpose without distracting from the main content. By adhering to best practices, content creators can maintain a professional appearance while optimizing user experience across various devices and platforms.
Careful consideration and strategic implementation of transitions can significantly impact the overall quality of digital presentations, videos, websites, and animations. This section provides essential guidelines and actionable tips to maximize the effectiveness of your transitions, ensuring they contribute positively to your content’s narrative and aesthetic.
Guidelines for Choosing Appropriate Transition Types
Choosing the right transition depends on the context, purpose, and tone of your content. Transitions should complement the narrative flow without overpowering it. For instance, subtle fades and dissolves are ideal for professional presentations, while dynamic slides or wipes may suit more energetic or creative projects. Consider the emotional response you wish to evoke and the compatibility with your overall design language.
Tip: Match transition styles with your content’s mood. For formal reports, opt for simple, unobtrusive transitions; for creative portfolios, experiment with more expressive effects.
Dos and Don’ts for Effective Transition Application
To ensure transitions enhance rather than distract, it is vital to follow certain best practices and avoid common pitfalls. The following list Artikels key dos and don’ts:
- Do: Use consistent transition styles throughout a project to maintain visual harmony.
- Do: Limit the number of different transition types used; a few well-chosen effects can be more impactful than many varied ones.
- Do: Ensure transitions are smooth and appropriately timed; abrupt or overly long transitions can disrupt the viewing experience.
- Don’t: Overuse flashy or complex transitions that may divert attention from the main content.
- Don’t: Rely solely on default transitions without customizing their duration and style to fit your content’s needs.
- Don’t: Neglect testing transitions on different devices, as effects may appear inconsistent or cause performance issues.
- Do: Keep accessibility in mind by avoiding overly rapid or distracting effects that could hinder users with visual sensitivities.
Methods for Testing Transitions Across Devices and Browsers
Ensuring that transitions perform consistently across various devices and browsers is essential for a professional and accessible presentation. Testing methods include both manual and automated approaches to detect discrepancies and optimize performance.
- Utilize cross-browser testing tools that simulate how your content appears on different browsers and operating systems. These tools often include options to preview animations and transitions in various environments, allowing for adjustments as needed.
- Perform real-world testing on multiple devices, including desktops, tablets, and smartphones, to observe how transitions render and whether they impact performance or user experience.
- Implement performance profiling tools to analyze the impact of transitions on load times and responsiveness, especially for web-based content. Tools like Chrome DevTools can help identify lag or rendering issues.
- Gather user feedback from diverse audiences to identify any inconsistencies or usability concerns that may not be evident through automated testing alone.
- Adjust transition durations, effects, and implementation techniques based on testing results to ensure they are smooth, unobtrusive, and compatible across platforms.
Troubleshooting Common Transition Issues
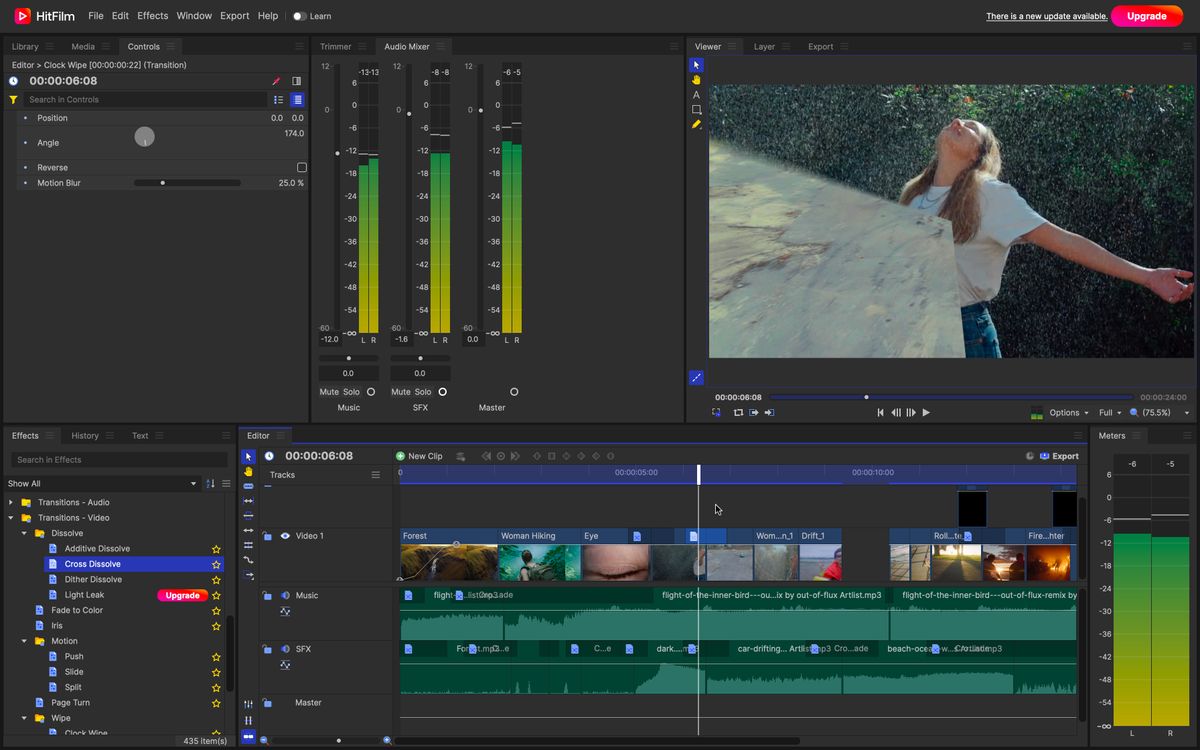
Transitions are essential elements that enhance visual flow and engagement in digital content. However, creators often encounter common problems such as lag, flickering, or abrupt changes that disrupt the viewer’s experience. Addressing these issues promptly ensures a seamless and professional appearance of the final product. This section provides diagnostic steps and solutions to identify and resolve typical transition-related problems effectively.Transitions can sometimes behave unpredictably due to various technical or implementation errors.
Understanding the root causes of these issues allows for targeted troubleshooting, minimizing unnecessary adjustments and optimizing performance across different platforms and devices.
Identifying and Resolving Transition Performance Problems
Effective troubleshooting begins with accurately diagnosing the underlying causes of transition issues. The following table organizes common problems, their potential causes, and corresponding fixes to streamline the problem-solving process.
| Problem Description | Cause | Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Lag or slow transition rendering during playback | High-resolution media, excessive transition effects, or hardware limitations |
|
| Flickering or visual tearing during transitions | Frame rate mismatch or insufficient refresh rate support |
|
| Transitions appear abrupt or choppy | Inadequate transition duration or improper easing |
|
| Unintended flickering or artifacts in web-based transitions | CSS or rendering conflicts, browser compatibility issues |
|
| Transitions not triggering or appearing inconsistently in presentations | Incorrect timing or transition settings in presentation software |
|
Implementing these diagnostic steps systematically facilitates the identification of root causes and enables efficient resolution of transition issues. Regular testing across different devices and platforms further ensures that transitions perform optimally in varied viewing environments.
Closing Notes
In summary, mastering how to add transitions empowers creators to craft polished and captivating content. By selecting appropriate effects and following best practices, you can deliver smooth visual journeys that captivate your audience and improve overall presentation quality.