Mastering how to rotate video clips is essential for achieving the desired visual presentation and enhancing viewer engagement. Whether correcting accidental orientations or creating creative effects, understanding the process helps streamline your editing workflow and ensures your videos look professional and polished.
This comprehensive guide explores various tools and techniques for rotating video clips, from simple adjustments in popular editing software to more advanced creative applications. By following step-by-step procedures, you can easily correct, enhance, and creatively manipulate your videos to fit your project’s needs.
Understanding Video Rotation
Video rotation is a fundamental editing technique that allows creators to change the orientation of their video clips to ensure proper viewing and aesthetic appeal. It plays a crucial role in correcting misaligned footage, enhancing visual storytelling, and maintaining consistency throughout a project. Properly rotating videos is essential in delivering a professional-quality output that aligns with the intended viewing experience and platform specifications.
In the context of video editing workflows, rotating clips involves adjusting their orientation to match desired visual presentation standards. Whether correcting accidental camera tilts, adapting content for different viewing devices, or creating dynamic visual effects, understanding the nuances of video rotation enhances the overall quality of the finished product. This process directly impacts viewer engagement by ensuring the content is easy to watch, correctly oriented, and visually appealing.
Angles of Rotation and Their Applications
The primary rotation angles used in video editing are 90 degrees clockwise, 90 degrees counterclockwise, 180 degrees, and sometimes arbitrary angles such as 45 or 135 degrees for creative effects. These angles serve specific purposes depending on the context of the footage and the desired outcome.
| Rotation Angle | Application |
|---|---|
| 90 Degrees Clockwise | Corrects footage shot in portrait mode or when the camera is tilted sideways, commonly used for mobile videos or portraits. |
| 90 Degrees Counterclockwise | Similar to the clockwise rotation but used when footage needs to be rotated in the opposite direction, often for correcting upside-down shots. |
| 180 Degrees | Flips the video upside down; useful for correcting inverted footage or creating mirror effects for artistic purposes. |
| Arbitrary Angles (e.g., 45°, 135°) | Used for creative effects or specific stylistic choices, such as simulating dynamic camera movements or abstract visual presentations. |
Rotating a video impacts its orientation by repositioning the visual content, which can significantly influence viewer perception. For example, a correctly oriented video ensures that viewers interpret the scene as intended, avoiding confusion or discomfort. Additionally, orientation plays a role in platform-specific requirements, such as vertical videos for social media stories or horizontal formats for cinematic appeal. Proper rotation thus enhances the viewer’s experience by aligning visual presentation with context and expectations.
Effective video rotation ensures the content’s clarity, aesthetic harmony, and platform compatibility, ultimately elevating viewer engagement and professional quality.
Tools and Software for Rotating Video Clips
When it comes to rotating video clips, selecting the appropriate software can significantly streamline the editing process. Many professional and free tools offer robust rotation features, making it accessible for both beginners and experienced editors to adjust their videos with precision. The choice of software often depends on factors such as ease of use, supported formats, and additional editing capabilities.
Understanding the options available allows users to choose the tool that best fits their workflow and project requirements. From feature-rich professional applications to straightforward online platforms, the diversity of tools ensures that everyone can find a suitable solution for rotating videos efficiently.
Popular Video Editing Software with Rotation Features
This section highlights some of the most widely used video editing tools that support video rotation. Each software caters to different user needs, from professional-grade applications to free and easy-to-access online tools.
| Software | Features | Ease of Use | Supported Formats |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adobe Premiere Pro | Advanced editing, multi-track timeline, precise rotation and transformation tools, extensive format support | Professional-grade, steep learning curve, extensive tutorials available | Supports a wide range including MP4, MOV, AVI, MXF, and more |
| Final Cut Pro | High-performance editing, keyframe-based rotation, multi-format support, seamless integration with Apple ecosystem | User-friendly for Mac users, intuitive interface, comprehensive documentation | Supports formats like MOV, MP4, AVI, and others |
| iMovie | Basic rotation tools, simple trimming, transitions, and effects, optimized for Mac and iOS devices | Very easy for beginners, drag-and-drop functionality | Supports MOV, MP4, and M4V formats |
| DaVinci Resolve | Professional color grading, multi-platform, precise rotation controls, extensive format support | Moderate learning curve, detailed tutorials available | Supports MP4, MOV, AVI, MXF, and more |
| Free Online Tools (e.g., Clideo, Kapwing) | Quick, browser-based editing, basic rotation and trimming features, no installation required | Very easy, suitable for quick edits without advanced features | Supports common web-compatible formats like MP4, WebM, MOV |
Importing Video Clips into Editing Platforms for Rotation
The process of importing video clips varies across software but generally follows a straightforward approach. Proper importing ensures that the clips are correctly loaded into the editing timeline, allowing for seamless rotation adjustments.
- Adobe Premiere Pro: Use the “Import” option in the File menu or drag the video file directly into the Project panel. Once imported, drag the clip onto the timeline for editing.
- Final Cut Pro: Click “File” > “Import” > “Media,” browse to locate your video file, and click “Import Selected.” The clip appears in the browser for easy placement.
- iMovie: Click the “Import Media” button, navigate to your video file, and select “Import.” Drag the imported clip into the timeline for rotation and other edits.
- DaVinci Resolve: Navigate to the “Media” workspace, right-click in the Media Pool, select “Import Media,” choose your clip, and then drag it into the timeline or edit page.
- Online Tools: Typically, upload your video directly through the web interface by clicking the upload button, selecting your file, and waiting for it to process before applying rotation.
Ensuring proper importation is crucial for maintaining video quality and facilitating accurate rotation adjustments across different editing environments.
Step-by-Step Procedures to Rotate Video Clips
Rotating video clips accurately and efficiently is essential for achieving professional-looking edits. Whether adjusting the orientation for better viewing or correcting improper recordings, understanding the precise procedures across different editing software ensures a seamless workflow. This section provides detailed, step-by-step instructions for rotating videos in major editing programs, covering common rotation angles such as 90 degrees clockwise, counterclockwise, and arbitrary angles.
Following these procedures will help users perform rotations with confidence, utilizing specific menu paths and shortcuts tailored to each software environment, thus streamlining the editing process and ensuring high-quality results.
Rotating Videos in Major Editing Programs
Below are comprehensive step-by-step instructions for rotating videos within popular editing platforms. Each guide emphasizes menu navigation, shortcut keys, and precise steps to execute rotations effectively for various angles.
| Software | Procedure for Rotating Videos |
|---|---|
| Adobe Premiere Pro |
|
| Final Cut Pro |
|
| DaVinci Resolve |
|
Rotating Videos by Specific Angles
Rotating videos by standard angles like 90 or 180 degrees is straightforward, but arbitrary rotations require precise input. These procedures enable accurate rotation adjustments, whether for correcting orientation or creatively altering the video presentation.
- Identify the rotation angle needed for your project, whether it’s a common 90-degree turn or a custom degree like 45 or 135.
- Access the rotation controls through the effect or transform panels in your editing software, as detailed above.
- Enter the specific degree value in the rotation input field. For clockwise rotation, input positive degrees (e.g., 45, 135). For counterclockwise, input negative degrees (e.g., -45, -135).
- Preview and adjust the rotation in real-time to verify the orientation matches your intent. Fine-tune the degree as necessary.
- Apply the rotation and render the clip to ensure the change is solidified in your final output.
Note: When rotating by arbitrary angles, ensure the video frame is resized or repositioned if necessary, as rotations can sometimes crop or shift content. Most editing programs offer options to scale or reposition clips post-rotation to maintain framing.
Adjusting Video Orientation and Position After Rotation
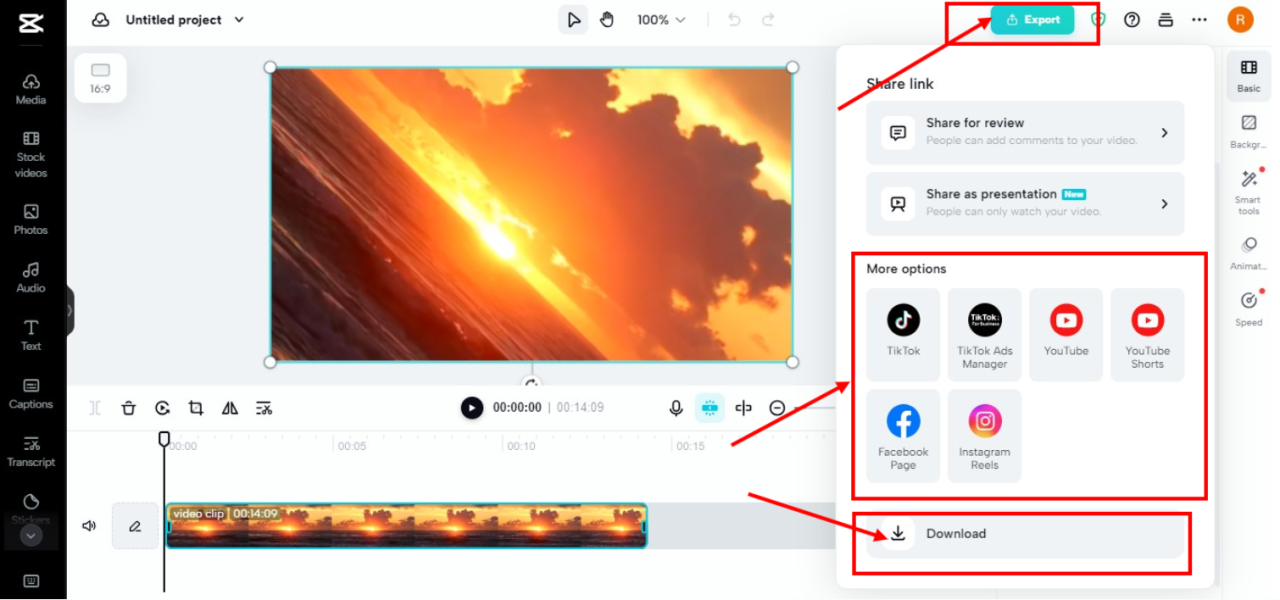
Rotating video clips often introduces challenges related to maintaining the correct aspect ratio, eliminating black bars, or preventing unwanted stretching. Proper adjustment ensures that the visual content remains appealing, professional, and true to the original composition. Mastering these techniques allows for seamless integration of rotated clips into your overall video project, enhancing viewer engagement and aesthetic consistency.Post-rotation adjustments are crucial because rotation alone can distort the video’s proportions or create visual artifacts such as black bars.
These issues arise due to differences in aspect ratios between the original footage and the display frame, especially when rotating by angles other than 90°, 180°, or 270°, which tend to preserve aspect ratios. Correcting these problems involves a combination of cropping, zooming, repositioning, or applying additional effects to optimize the visual presentation.
Techniques for Fixing Aspect Ratio Issues, Black Bars, or Stretching
When a video is rotated, especially at arbitrary angles, black bars may appear along the sides or top and bottom, detracting from the overall visual quality. To address these challenges, several techniques are applicable:
Adjusting the aspect ratio entails either cropping the black bars or resizing the video to fit within the display frame without distortion. Cropping involves trimming the edges of the video to remove black borders, resulting in a more focused view. Resizing or scaling can be used to fit the content to a specific aspect ratio, but must be done carefully to prevent stretching or squashing.
Stretching occurs when the aspect ratio is altered inadvertently during resizing. To avoid this, it’s important to maintain the original aspect ratio by locking the aspect ratio setting in your editing software. This ensures that the video scales proportionally, preserving the visual integrity of the content.
Techniques such as letterboxing, pillarboxing, cropping, and zooming are vital to maintain quality after rotation.
Methods to Crop, Zoom, or Reposition Clips Post-Rotation
Once a video has been rotated, further adjustments are often necessary to ensure the content looks natural and visually appealing. The following methods help optimize the presentation:
- Cropping: Use cropping tools to remove unwanted black bars or stretched edges. Cropping is especially effective when the rotated footage introduces black areas due to aspect ratio mismatch. For example, cropping the top and bottom of a 16:9 video rotated at an angle can eliminate black borders, creating a clean, rectangular frame.
- Zooming: Applying a digital zoom can enlarge the central portion of the video, compensating for black borders or framing issues. While zooming reduces the visible area, it allows maintaining a full-screen display without black bars. It is important to balance zoom levels to prevent pixelation and loss of quality.
- Repositioning: Moving the video clip within the frame—adjusting its position horizontally or vertically—can help center the subject or key elements, especially after rotation. This is useful for emphasizing specific areas or correcting misaligned compositions.
Modern video editing software often provides intuitive controls for cropping, zooming, and repositioning. For example, using keyframes allows smooth transitions between different framing setups, creating dynamic effects or correcting alignment throughout the clip.
Combining Rotation with Other Editing Effects for Seamless Adjustments
Integrating rotation adjustments with other effects enhances the overall visual coherence of a video project. For instance:
- Applying Perspective or Warp Effects: After rotation, minor perspective corrections can help align the scene, especially if the rotation caused skewed angles or distortions. These effects simulate camera adjustments, improving realism.
- Using Color Correction and Filters: Post-rotation color grading can unify the look of clips that may appear mismatched due to framing adjustments. Filters can also be used to emphasize certain areas or add stylistic effects that complement the rotation.
- Utilizing Motion and Transition Effects: When repositioning or zooming, motion effects like pan or zoom can create smooth, professional-looking transitions that mask abrupt framing changes. This approach ensures that viewers remain engaged without noticing technical adjustments.
For example, rotating a landscape shot by 45° might introduce black borders. Cropping and zooming into the scene, combined with slight color corrections and a gentle pan effect, can produce a visually harmonious result suitable for professional presentations or cinematic projects.
Exporting Rotated Videos
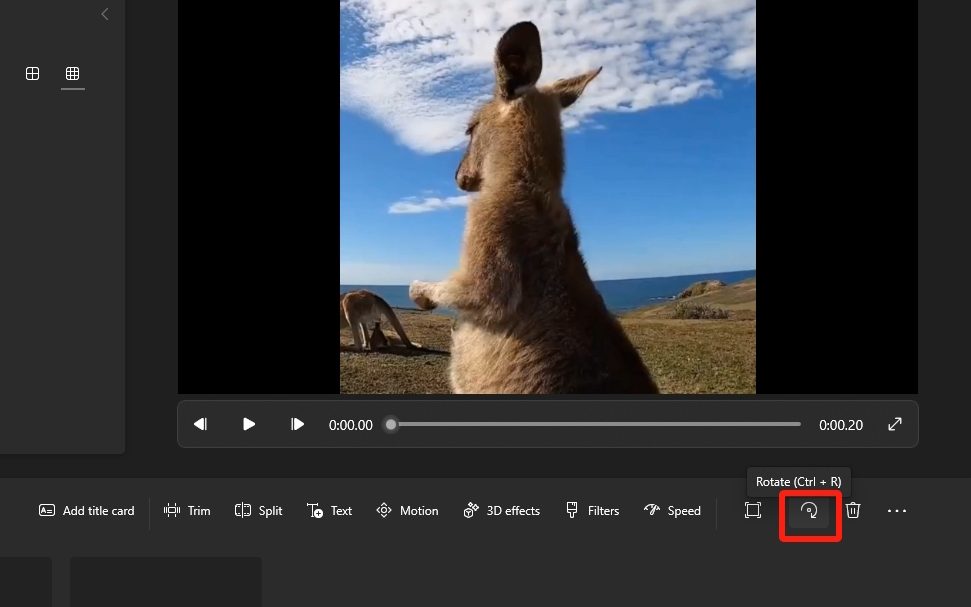
Once you have successfully rotated your video clips and adjusted their orientation and positioning, the next critical step is exporting the final version. Proper exporting ensures that the quality and integrity of your video are maintained while making it suitable for your intended platform or purpose. This phase involves selecting appropriate formats, settings, and additional metadata to protect and optimize your content for viewers across various channels.
Effective export procedures are essential to achieve high-quality results and efficient playback, whether you’re sharing videos on social media, embedding them on websites, or preparing broadcast content. Understanding the best practices for exporting can help prevent common issues such as pixelation, color loss, or large file sizes, which can hinder viewer engagement or distribution efforts.
Best Practices for Exporting Videos to Preserve Quality
Maintaining the visual and audio quality of your rotated videos during export is paramount. Adhering to certain best practices can significantly enhance the final output:
- Use the original source resolution and avoid unnecessary compression that reduces clarity.
- Choose a high bit rate tailored to your video’s resolution and complexity; higher bit rates typically produce better quality but result in larger files.
- Opt for lossless or minimally compressed codecs like H.264 or H.265 (HEVC), which balance quality and file size effectively.
- Set the frame rate to match the original footage unless specific adjustments are needed for the target platform.
- Preview the exported video to ensure no loss of detail or artifacts occur after processing.
Common Formats and Settings for Different Platforms
Different platforms have specific requirements and optimal settings to ensure your video appears professional and plays smoothly. Selecting the right format and configuration depends on the destination of your video:
| Platform | Recommended Format | Key Settings |
|---|---|---|
| Social Media (e.g., Instagram, Facebook, TikTok) | MP4 (H.264 codec) | Resolution: 1080×1080 or 1920×1080; Frame rate: 30 fps; Bit rate: 8-12 Mbps; Aspect ratio: 1:1 or 16:9 |
| Web Embedding or Streaming | MP4 (H.264 or H.265) | Resolution: 1920×1080; Frame rate: 30 fps; Bit rate: 10-20 Mbps; Codec: H.264 or H.265 |
| Broadcast or Professional Use | MOV or MXF (ProRes or DNxHD codecs) | High bit rate; Resolution: 4K or HD; Frame rate: 24 or 30 fps; Color depth: 10-bit for color grading flexibility |
“Choosing the correct export settings tailored to your distribution platform ensures optimal playback quality and viewer engagement.”
Adding Metadata and Watermarks During Export
Incorporating metadata and watermarks into your exported videos enhances security, branding, and content management. Metadata includes information such as copyright details, author, description, and s, which can help with searchability and rights management. Watermarks serve as visual identifiers that protect your content from unauthorized use or distribution.
During the export process, most video editing or conversion software provides options to embed metadata directly into the video file. This can include standard tags, descriptive information, and licensing details. Watermarks can be added as overlay graphics, logos, or semi-transparent text placed strategically to avoid obstructing critical visual elements while remaining visible enough to deter theft.
| Features | Implementation |
|---|---|
| Metadata Addition | Fill in fields such as title, author, copyright, and description within the export settings or metadata editor of your software. |
| Watermark Embedding | Import a logo or text overlay and position it in a corner or along the border; adjust opacity and size for subtle branding or deterrence. |
Properly embedding metadata and watermarks at the export stage ensures your content remains protected and properly attributed, especially when sharing on public platforms or distributing to clients.
Troubleshooting Common Rotation Issues
Rotating video clips can sometimes lead to unexpected problems that affect the final quality of your footage. Addressing these issues promptly ensures your videos maintain their professional appearance and synchronization. Understanding common rotation challenges and solutions can save time and prevent frustration during post-production.When modifying video orientation, issues such as distorted aspect ratios or audio-video sync problems frequently occur. These problems can stem from incorrect software settings, incompatible formats, or improper export configurations.
Recognizing the root causes helps in applying effective remedies and achieving a seamless viewing experience.
Aspect Ratio Distortion and Resolution Problems
When rotating videos, maintaining the correct aspect ratio is essential to prevent distortion or stretching that can compromise visual quality. Incorrect settings or unsupported formats can cause videos to appear stretched horizontally or vertically, disrupting the intended composition.To resolve aspect ratio distortions, it is vital to:
- Ensure the rotation settings preserve the original aspect ratio, typically by selecting options like “Maintain Aspect Ratio” or “Fit to Frame.”
- Verify output resolution matches the original or desired display dimensions before exporting.
- Use video editing software that automatically adjusts the canvas size or offers aspect ratio locking features to prevent distortion.
Properly configuring export settings and previewing the video before final rendering are best practices to avoid aspect ratio issues post-rotation.
Audio-Video Synchronization Issues
Rotation can sometimes lead to desynchronized audio and video tracks, especially in formats where timing information is tightly coupled with the video stream. This misalignment results in audio lagging behind or running ahead of the visual content, impacting viewer comprehension and overall quality.To address synchronization problems:
- Check the original video’s audio and video tracks for synchronization issues prior to rotation.
- Use software that preserves audio sync during rotation processes, or re-sync audio manually after rotation using timeline editing features.
- If available, enable “Maintain Audio Sync” options within the rotation or export settings to prevent desynchronization.
- Test the rotated clip by playing it within the software and on different media players to ensure consistency.
Regular testing before exporting the final version helps catch sync issues early and allows for timely corrections.
Best Practices for Testing and Validation
Ensuring the quality of rotated videos involves thorough testing during the editing process. Even after applying rotation adjustments, it is crucial to review the video thoroughly to identify and rectify any issues before exporting.Key testing tips include:
- Preview the entire clip in the editing software’s playback window, paying close attention to transitions, aspect ratio, and synchronization.
- Export a short sample or draft version with the current settings and review it on different media players and devices to verify compatibility and quality.
- Use calibrated monitors or screens to accurately assess visual fidelity and detect any distortion or artifacts introduced during rotation.
- Compare the rotated version with the original footage to ensure that no crucial details are lost or compromised during the process.
Implementing these testing procedures reduces the risk of exporting flawed videos and ensures consistent quality in the final product.
Creative Uses of Video Rotation
Video rotation is not only a technical adjustment but also a powerful creative tool that can significantly enhance visual storytelling. When used thoughtfully, rotation techniques can introduce dynamic effects, evoke specific moods, or create artistic visuals that captivate viewers. Exploring the creative potential of video rotation opens up new avenues for video editors and content creators to craft engaging and memorable projects with visual innovation.Rotation effects can be combined with other transformations such as scaling, translation, or color correction to produce complex visual compositions.
By layering these effects, creators can produce seamless transitions, simulate different camera angles, or emphasize particular elements within a scene. The artistic combination of rotation with color grading, for example, can evoke a vintage or futuristic aesthetic, while blending rotation with scaling can create zooming effects that add depth and motion to static shots.Innovative video projects have leveraged rotation techniques to produce visually stunning results.
For instance, music videos often employ creative rotation effects to generate a sense of movement and energy that aligns with the rhythm. Similarly, promotional videos for products or brands use rotation effects to highlight features dynamically, making static objects appear more engaging. Artistic films and experimental video art frequently utilize rotation to distort perspectives, challenge viewers’ perceptions, or craft surreal visuals that stand out in a crowded media landscape.
Dynamic Transitions and Artistic Visuals
The use of rotation as a transition effect can introduce a sense of movement and fluidity between scenes. For example, a 360-degree spin can serve as a transition from one shot to another, creating a seamless and engaging shift that maintains viewer interest. This technique can be enhanced by timing the rotation to music beats or narrative cues, adding a rhythmic element to the visual flow.Rotation can also be employed to produce artistic visuals that break away from conventional framing.
By rotating a scene or object, creators can simulate a turning point or evolving narrative perspective. For instance, rotating a shot of a city skyline to gradually reveal a different time of day or weather condition adds artistic depth and storytelling layers.Combining rotation with other transformations further enriches the visual effect. Scaling during rotation can produce zoom-in or zoom-out effects that dramatize a subject, while color correction applied concurrently can evoke specific moods or themes.
For example, a slow rotation combined with desaturation and a vignette can create a somber, contemplative atmosphere, ideal for artistic or documentary projects.
“Creative video rotation blends technical precision with artistic vision, transforming simple adjustments into compelling visual stories.”
The versatility of rotation effects in video editing enhances the creative toolkit of editors, empowering them to produce innovative and visually compelling content that resonates with audiences and elevates their projects to new heights.
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, mastering how to rotate video clips opens up a wide range of possibilities for editing and creative expression. Whether fixing orientation issues or adding artistic effects, the techniques discussed empower you to produce visually appealing videos with confidence. Remember to experiment with different tools and settings to find what best suits your project goals.