Learning how to add captions to video is a vital skill for content creators, educators, and professionals aiming to increase accessibility and audience reach. Captions not only support viewers with hearing impairments but also enable viewers to enjoy content in sound-off environments or noisy settings. Understanding the different formats, tools, and best practices involved in captioning ensures that your videos are inclusive, compliant, and engaging for all viewers.
Understanding the Basics of Adding Captions to Video
In the realm of digital video content, adding captions serves as a vital enhancement to improve accessibility, comprehension, and audience reach. Captions provide a text-based representation of spoken words, sounds, and important audio cues, making videos more inclusive for viewers with hearing impairments and viewers in sound-off environments such as public spaces or noisy settings.
Understanding the foundational elements of caption integration is essential for content creators, broadcasters, and educators seeking to optimize their videos for diverse audiences. This overview covers the primary purposes, common formats, and supported platforms that facilitate efficient captioning processes.
Purpose and Benefits of Adding Captions to Videos
Adding captions to videos significantly broadens accessibility, ensuring that individuals with hearing disabilities can engage fully with multimedia content. Beyond accessibility, captions enhance viewer understanding, especially in situations where audio clarity is compromised or language barriers exist. They also improve performance by enabling search engines to index spoken content, thereby increasing the discoverability of videos.
Furthermore, captions support viewers in noisy environments such as public transport or gyms, where audio playback might be inconvenient. They also serve educational purposes by reinforcing language learning and comprehension, making captions a versatile tool across various sectors.
Common Formats and Standards for Caption Files
Caption files adhere to specific formats and standards that facilitate compatibility across platforms and devices. The most prevalent formats include:
- SRT (SubRip Subtitle): A widely used plain-text format that includes time codes and subtitle text. Its simplicity and broad compatibility make it popular for online videos and editing tools.
- VTT (WebVTT): Designed specifically for web use, this format supports styling, positioning, and metadata, making it suitable for HTML5 videos and streaming services.
- SBV (YouTube Subtitle Format): Similar to SRT, used primarily within YouTube’s captioning system, emphasizing simplicity and ease of use.
- TTML (Timed Text Markup Language): An XML-based standard used mainly in professional broadcasting and streaming platforms, allowing for more complex styling and formatting options.
Choosing the appropriate caption format depends on the intended platform and the level of styling or metadata required. Compatibility and ease of editing should guide the selection process.
Platforms and Software Supporting Caption Integration
The proliferation of video distribution channels has led to the development of numerous platforms and software that support caption addition and management. These include:
| Platform/Software | Features |
|---|---|
| Adobe Premiere Pro | Professional editing suite with robust captioning tools supporting multiple formats, including SRT and VTT, with options for styling and positioning. |
| Final Cut Pro | Offers integrated captioning features, enabling creators to embed captions directly into their timelines and export in various formats. |
| YouTube | Supports automatic captioning with the option for manual editing, enabling creators to upload caption files or generate captions directly on the platform. |
| VLC Media Player | Supports loading external caption files during playback, facilitating testing and viewing of captioned videos. |
| Amara | Web-based platform designed for community-driven captioning, offering easy tools for creating, editing, and syncing captions across multiple videos. |
| Kapwing | Online video editor with straightforward captioning features, allowing automatic or manual addition of captions, export in multiple formats, and easy sharing. |
Preparing Caption Files for Your Video
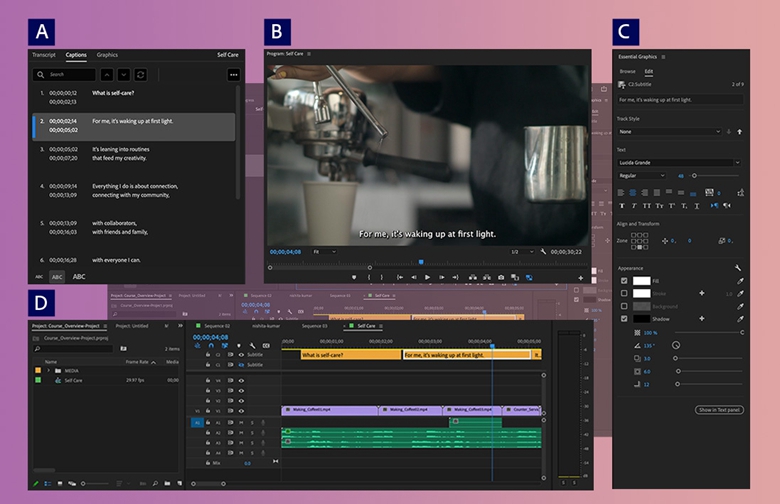
Creating accurate and well-structured caption files is a crucial step in enhancing the accessibility and viewer experience of your videos. Proper preparation ensures that captions synchronize seamlessly with the audio content, making your videos more inclusive for all audiences, including those with hearing impairments or language barriers. Understanding the process of developing effective caption files facilitates smoother integration with various video platforms and improves overall engagement.
In this section, we will explore the fundamental steps involved in manually creating caption text files, techniques for synchronizing captions with video timestamps, organizing caption data effectively, and best practices for formatting captions to maximize clarity and accessibility.
Creating Accurate Caption Text Files Manually
Developing caption files begins with transcribing the spoken content of your video into text. Accuracy is vital to ensure viewers receive the correct information, especially for technical or detailed content. Start by watching the video multiple times, noting down spoken words, sound effects, and important contextual cues. It is recommended to use simple text editing software, such as Notepad or TextEdit, to create plain text files, which are compatible with most caption formats like SRT or VTT.
Each caption entry should include the exact dialogue or description, avoiding ambiguity or abbreviations that could confuse viewers. Break long sentences into smaller, digestible segments, typically around 2-3 lines per caption, to improve readability. Additionally, include cues for sound effects or speaker identification when necessary to provide full context, especially in scenes with overlapping dialogue or background noise.
Synchronizing Captions with Video Timestamps
Accurate synchronization between captions and video timing is essential for a cohesive viewing experience. To achieve this, use media players or caption editing tools that allow you to mark precise in and out points for each caption segment. Play the video and pause at significant moments to note the exact timestamps, then input these into your caption file. Most caption formats require start and end times in hours, minutes, seconds, and milliseconds, such as 00:01:15,000 –> 00:01:18,500.
For complex videos, consider adopting a systematic approach by dividing the timeline into manageable segments, ensuring that captions appear and disappear at appropriate times. This method helps prevent lag or premature display of text, which can distract viewers or cause confusion. Regularly preview your captions alongside the video to verify synchronization accuracy and make necessary adjustments to timestamps.
Organizing Caption Data Using HTML Tables
Effectively organizing caption attributes enhances clarity and simplifies the editing process. Using HTML tables allows you to systematically arrange key data, such as caption text, start time, end time, and speaker or sound cues. A typical table structure with four columns might include:
| Caption Text | Start Time | End Time | Attributes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Welcome to our presentation. | 00:00:05,000 | 00:00:08,000 | Speaker: Host |
| Let’s discuss the agenda. | 00:00:08,500 | 00:00:12,000 | Sound: Applause |
Employing such organized structures aids in editing, reviewing, and ensuring each caption’s timing and content are accurate and appropriately formatted. This approach also facilitates easier updates or corrections during the caption creation process.
Best Practices for Formatting Captions for Clarity and Accessibility
Formatting captions effectively enhances readability and ensures they serve their primary purpose—delivering information clearly. Use a consistent font size and style, typically a simple, legible font such as Arial or Verdana. Keep captions concise, ideally no longer than two lines or 42 characters per line, to prevent viewer fatigue.
“Captions should be easily readable within the video’s context, avoiding clutter and excessive text.”
Apply proper punctuation, grammar, and spelling to maintain professionalism and prevent misunderstandings. Include sound cues within brackets, such as [music playing], [door creaks], or [laughter], to provide additional context. When indicating different speakers, consider adding labels like Speaker A: or Host: before the dialogue to clarify who is speaking.
Maintain consistent timing intervals and avoid overlapping captions unless intentionally designed for simultaneous dialogue. When working with different caption formats, adhere to their specific syntax requirements, such as ensuring timestamps are in the correct format and text encoding is set to UTF-8 to support special characters or accents.
Methods to Add Captions Using Video Editing Software
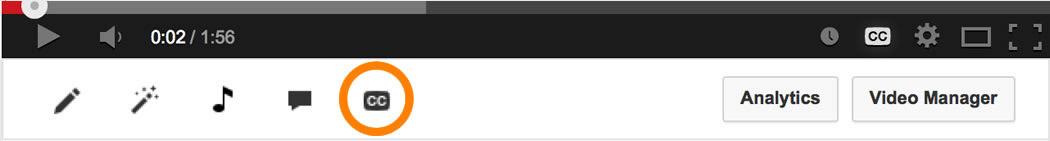
Integrating captions directly into your video enhances accessibility and viewer engagement. Using professional editing software provides precise control over caption placement, style, and timing, ensuring a polished final product. This section guides you through importing caption files, embedding captions within your video timeline, and exporting your project with embedded or separate caption tracks. Additionally, a comparison of popular editing platforms highlights their features and user-friendliness, helping you choose the best tool for your needs.
Importing Caption Files into Video Editing Tools
Most top-tier video editing software supports importing caption files in formats such as SRT, VTT, or SCC. Proper importation is crucial for accurate synchronization and ease of editing. When importing, ensure that the caption file aligns with your video’s timeline and that the timing is preserved correctly. This process allows you to review and fine-tune captions before embedding or exporting them with your video.
For example, in Adobe Premiere Pro, you can import caption files by navigating to the Media Browser, right-clicking to select Import, and choosing your caption file. The caption track then appears in your project panel. In Final Cut Pro, captions are imported through the File > Import > Captions option, which automatically adds the captions to your timeline, ready for further editing or embedding.
Embedding Captions Directly into the Video Timeline
Embedding captions directly involves placing them on the timeline as a track synchronized with your video footage. This method ensures the captions are permanently integrated into the video, making them visible in any media player that supports embedded captions. It also allows for creative adjustments such as positioning, styling, and timing modifications within the editing environment.
In practice, you can drag and drop caption files onto the timeline or create caption layers manually. Adjustments can be made to the timing to match spoken words or action sequences accurately. For instance, in Adobe Premiere Pro, after importing captions, you can convert caption files into caption layers, then position and style each caption segment as needed. Final Cut Pro offers similar functionalities, enabling seamless caption integration directly into the editing workflow.
Exporting Videos with Embedded or Separate Caption Tracks
Export options vary depending on the desired delivery format and platform requirements. When exporting, you can choose to embed captions directly into the video stream, making them part of the video file, or export captions as separate tracks, which can be toggled on or off during playback.
In Adobe Premiere Pro, the Export Settings menu provides options for including captions—either as burned-in (hardcoded) captions or as a sidecar file (e.g., SRT). Burning in captions ensures they are always visible, while separate caption tracks offer flexibility for platforms that support selectable captions.
Similarly, Final Cut Pro allows exporting with embedded captions through specific settings or exporting the caption track separately as a sidecar file. These options are crucial for compliance with accessibility standards and for providing viewers with customizable caption options.
Comparison of Features and Ease of Use Across Platforms
Choosing the right editing platform depends on your workflow, familiarity, and the specific features needed for captioning. Adobe Premiere Pro stands out for its robust caption support, extensive format compatibility, and detailed styling options, making it suitable for professional projects. Final Cut Pro offers an intuitive interface with efficient caption importing and embedding workflows, ideal for Mac users. DaVinci Resolve provides a free option with solid captioning capabilities, although it may lack some advanced features of paid tools.
“Ease of use varies; Premiere Pro’s comprehensive tools are perfect for detailed projects, while Final Cut Pro offers streamlined processes for faster workflows. Both support exporting captions either embedded or separately, catering to diverse platform requirements.”
In summary, the choice of software depends on your project scope, budget, and platform preferences. All these tools facilitate accurate caption integration, ensuring your videos meet accessibility standards and reach a broader audience.
Uploading Captions to Video Hosting Platforms
Providing captions enhances accessibility, user engagement, and compliance with platform policies. Uploading captions correctly ensures viewers can enjoy your content with accurate subtitles, regardless of their hearing ability or language barriers. Each platform has specific procedures for adding captions, which, when followed properly, streamlines the process and minimizes technical issues.Accurate caption uploads are critical for ensuring that subtitles display correctly and synchronize seamlessly with the video.
Mistakes or omissions during upload can lead to caption misalignment or display errors, reducing viewer satisfaction and accessibility compliance. Therefore, understanding the specific steps for each platform is essential for smooth integration.
YouTube
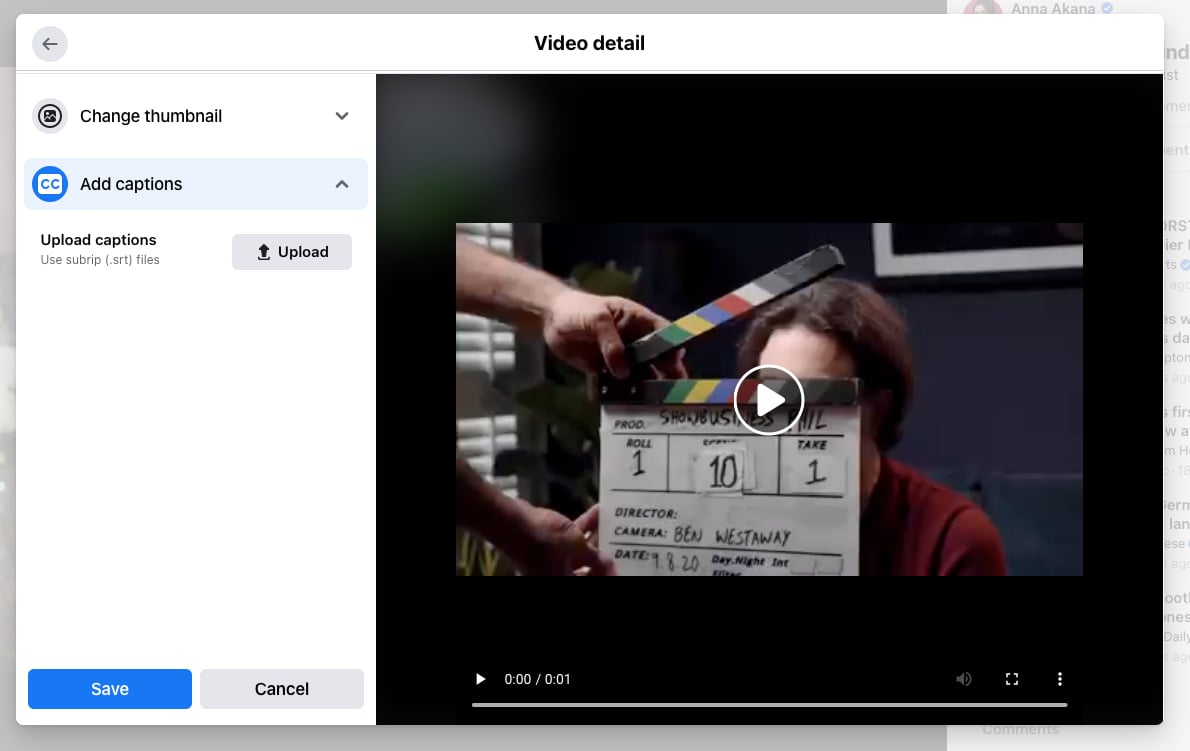
YouTube offers straightforward options for adding captions during the upload process or via editing existing videos. The platform supports multiple caption formats, including .srt, .sub, and .vtt files. Properly uploading captions involves the following steps:
- Sign in to your YouTube Studio account and navigate to the “Content” section.
- Select the video to which you want to add captions.
- Click on the “Subtitles” tab in the left menu.
- Click the “Add Language” button, then choose your language.
- Under the language, click “Add” next to “Subtitles.”
- Select “Upload File” and choose the caption file from your device.
- Ensure the timing and synchronization are correct, then click “Publish.”
To add captions during video upload:
- Upload your video as usual.
- During the processing stage, navigate to the “Subtitles” tab.
- Select the language and upload your caption files following the above steps.
Troubleshooting tips include verifying caption file encoding (preferably UTF-8), checking for formatting errors in the caption file, and previewing captions before publishing to ensure proper synchronization.
Vimeo
Vimeo allows users to incorporate captions by uploading separate caption files during the video upload or editing process. Accurate caption integration is vital for ensuring accessibility and viewer comprehension. The workflow involves:
- Sign in to your Vimeo account and open the video manager.
- Upload your video if not already uploaded.
- Click on the video thumbnail and select “Settings.”
- Navigate to the “Advanced” tab, then select “Distribution.”
- Scroll to the “Captions” section and click “Add captions.”
- Upload your caption file in supported formats such as .vtt or .srt.
- Assign the appropriate language and save changes.
Adding captions during the upload process ensures they are embedded or linked properly, making them accessible to viewers. Common issues include mismatched timestamps or unsupported file formats, which can be resolved by validating captions with caption editing tools before upload.
Facebook offers a simple method for adding captions, especially for videos uploaded directly to a page or profile. Captions can be uploaded alongside the video during the upload process, which is essential for ensuring they appear correctly during playback.
- Log into your Facebook account and go to your page or profile.
- Click “Create Post” and upload your video file.
- Once the video starts uploading, click the “Add Captions or Subtitles” option if available.
- Choose “Upload SRT file” to add your captions or subtitles.
- Select the caption file from your device, then specify the language.
- Finish uploading the video and captions, then publish.
For videos already uploaded, you can go to the video post, select “Edit Video,” and add captions through the caption upload section. Troubleshooting often involves ensuring the caption file matches the video’s timing precisely and is in a supported format like .srt or .vtt.
HTML Markup for Caption Integration in Embedded Videos
Embedding videos with captions using HTML involves incorporating the `
<video width="640" height="360" controls> <source src="your-video.mp4" type="video/mp4"> <track src="captions-en.vtt" kind="subtitles" srclang="en" label="English"> Your browser does not support the video tag. </video>
In this example:
-The `
-The `
By following these procedures and tips, you can effectively upload and troubleshoot captions on multiple platforms, ensuring your videos are accessible, engaging, and compliant with accessibility standards.
Accessibility and Compliance Considerations
Ensuring that videos are accessible to all viewers and adhere to legal standards is a crucial aspect of captioning. As organizations and content creators aim to reach diverse audiences, understanding the legal requirements and best practices for caption accessibility becomes essential. Properly implemented captions not only enhance user experience but also fulfill regulatory obligations across different regions.
Captions play a vital role in making video content inclusive, particularly for individuals who are deaf or hard of hearing, those with cognitive disabilities, or viewers in sound-sensitive environments. To maximize accessibility, it is important to align captioning practices with established standards and legal mandates, which vary depending on geographical jurisdiction and platform policies.
Legal Requirements for Captions in Different Regions
Different countries enforce distinct regulations surrounding captioning and audiovisual accessibility. For example, in the United States, the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) and the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) mandate that publicly accessible video content must be captioned to serve individuals with disabilities. Similarly, the European Union’s Audiovisual Media Services Directive (AVMSD) emphasizes accessibility obligations for broadcasters and on-demand services, requiring captions for certain content.
In Canada, the Accessible Canada Act mandates that federally regulated entities provide accessible digital content, including accurate captions. Australia’s Disability Discrimination Act (DDA) and the Disability Standards for Education and other regulations also emphasize captioning as a best practice.
Compliance with regional legal standards typically involves ensuring that captions are accurate, synchronized, and available in formats compatible with various devices and platforms. Failure to meet these requirements can result in legal penalties, reputational damage, and reduced audience reach.
Ensuring Captions Meet Accessibility Standards
Adhering to established accessibility standards, such as the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.1, is fundamental for creating inclusive video content. WCAG emphasizes principles like perceivability, operability, understandability, and robustness, which directly influence caption quality.
To align with these standards, captions should:
- Be synchronized accurately with spoken dialogue and important sounds.
- Use a clear and legible font, with sufficient size and contrast against the background.
- Avoid complex or stylistic fonts that hinder readability.
- Display captions for an adequate duration to allow viewers sufficient time to read, typically at a rate of around 15 characters per second.
- Provide descriptions of non-verbal sounds or cues that are essential for understanding the context.
Implementing these practices enhances accessibility and ensures compliance with legal and technical standards, thereby broadening the reach of your content.
Importance of Caption Accuracy, Timing, and Readability
The effectiveness of captions hinges on their accuracy, timely delivery, and ease of reading. Inaccurate captions can lead to misunderstandings and diminish the viewer’s experience. For instance, misrepresenting a critical instruction or emotional nuance can negatively affect the content’s impact.
Timing is equally crucial; captions must appear in sync with the audio, avoiding delays that cause confusion or cut off essential information. Proper timing ensures that viewers can follow along seamlessly, which is particularly important during fast-paced dialogues or complex scenes.
Readability depends on font choice, size, color contrast, and the length of caption lines. Overly long lines can be difficult to read quickly, so best practices suggest keeping each caption line to approximately 32-40 characters and limiting each caption to two lines on the screen at a time. Clear, simple language also enhances comprehension across diverse audiences.
Methods for Testing Captions Across Devices and Users
To verify that captions meet accessibility standards and function correctly across various devices, comprehensive testing is essential. Testing methods include:
- Device Compatibility Checks: Testing captions on different devices such as desktops, tablets, smartphones, and smart TVs to ensure consistent display, font readability, and synchronization.
- Platform Validation: Ensuring captions function correctly across various platforms like YouTube, Vimeo, Facebook, and proprietary hosting solutions, considering platform-specific captioning features.
- Assistive Technology Compatibility: Using screen readers, magnifiers, and other assistive tools to verify that captions are compatible and accessible for users relying on such technologies.
- User Testing with Diverse Audiences: Gathering feedback from users with disabilities or diverse language backgrounds to identify potential issues related to readability, timing, or comprehension.
- Automated and Manual Checks: Employing automated tools to detect timing errors, misalignments, or formatting issues, supplemented by manual reviews to ensure contextual accuracy and clarity.
Regular testing across different configurations helps identify and resolve accessibility issues, ensuring that all viewers can benefit from your video content fully and reliably.
Advanced Captioning Techniques and Tools
Enhancing video accessibility and viewer engagement often requires moving beyond basic captions. Advanced captioning techniques and specialized tools enable creators to customize and enrich their captions, ensuring they are both functional and visually appealing. This segment explores the procedures for customizing caption styles, incorporating speaker identification and sound effects, organizing captioning tools, and leveraging speech recognition software for automation.
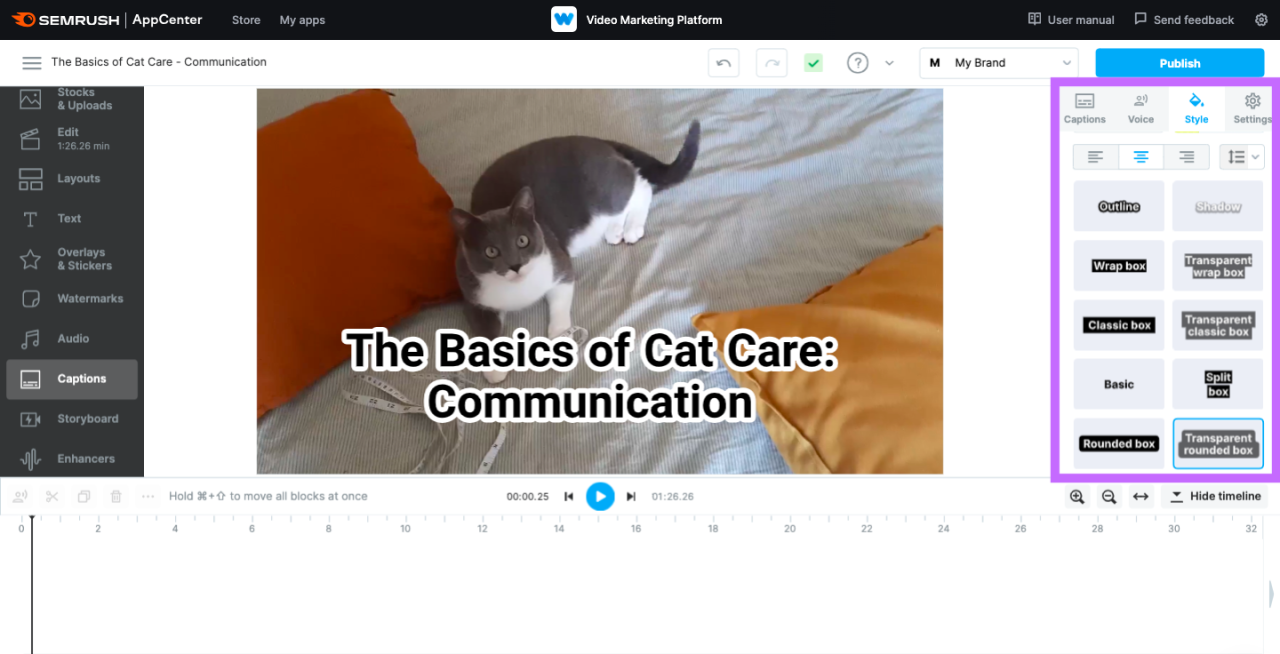
Customizing Caption Styles (Font, Size, Color)
Personalizing caption appearance allows for better readability and alignment with branding or aesthetic preferences. Adjusting font, size, and color contributes to a more professional and viewer-friendly presentation. These customizations can be performed within most modern video editing and captioning software, offering a range of options to match content tone and target audience needs.
Key parameters to customize include font family, font size, text color, background color, and Artikel style. Consistency in style enhances viewer comprehension, especially for viewers with visual impairments.
To customize caption styles effectively:
- Select the caption styling or formatting panel within your editing tool.
- Choose a legible font that complements your video content; common choices include Arial, Helvetica, or Open Sans.
- Set font size to ensure readability across different devices, typically between 18-24 pixels.
- Apply colors that contrast well with the video background; for instance, white or yellow text on dark backgrounds.
- Use background shading or Artikels sparingly to enhance text visibility without distracting from the video.
- Preview the captions to ensure styles are consistent and accessible across the entire video.
Adding Speaker Identification and Sound Effects in Captions
Including speaker labels and sound cues improves comprehension, especially in dialogues or complex scenes. Proper identification ensures viewers can follow conversations, identify who is speaking, and understand audio cues such as music or sound effects.
Speaker labels are typically formatted as “Speaker Name:” at the start of a caption line. Sound effects can be enclosed in brackets, e.g., [door creaks], to indicate ambient sounds.
Implementation steps:
- Identify segments where speaker changes occur or where sound effects are significant.
- Insert speaker labels before the corresponding dialogue, ensuring clarity and consistency.
- Use brackets to denote sound effects, with descriptive labels that accurately reflect the sounds.
- Maintain uniformity in formatting to help viewers easily distinguish speakers and sounds throughout the video.
- Review the captions to confirm accurate placement and clarity of speaker identification and sound cues.
Organizing Different Captioning Tools and Their Features
Knowledge of available captioning tools and their capabilities helps in selecting the most suitable software for specific projects. The following table summarizes popular captioning tools, highlighting their key features and unique advantages.
| Tool Name | Supported Formats | Automation Features | Customization Options | Platform Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adobe Premiere Pro | .SRT, .VTT, .CC | Manual and semi-automatic captioning, speech-to-text integration via plugins | Extensive styling options, speaker labels, sound effects | Windows, macOS |
| Final Cut Pro | .SRT, .XML | Manual caption editing, plugin support for automation | Custom styles, positioning, and timing adjustments | macOS |
| Amara | .VTT, .SRT, embedded captions | Automatic captioning with speech recognition, collaborative editing | Simple styling, translation features | Web-based platform |
| Rev.com | .SRT, .VTT, captions for streaming | Human and AI-generated captions, fast turnaround | Basic styling, speaker labels included | Web-based, integrations with other platforms |
This organized overview assists users in selecting tools that align with their project requirements, whether prioritizing automation, customization, or ease of use.
Automating Caption Generation with Speech Recognition Software
Automation significantly reduces the time and effort involved in caption creation, particularly for lengthy videos or frequent content updates. Speech recognition software leverages machine learning algorithms to convert spoken words into text with increasing accuracy.
While speech recognition tools are highly effective, they may require manual correction to address inaccuracies, especially with overlapping speech, accents, or background noise.
Best practices for automating caption generation include:
- Selecting reliable speech recognition software such as Otter.ai, Descript, or the built-in features in platforms like YouTube or Adobe Premiere Pro.
- Uploading or syncing your video to the tool for transcription processing.
- Reviewing and editing the generated captions to correct errors and add speaker labels or sound effects as needed.
- Utilizing customization options within the software to match caption styles and formatting preferences.
- Exporting the finalized caption files in appropriate formats compatible with your publishing platform.
Implementing these techniques accelerates the captioning process and enhances overall accessibility, making content more inclusive and engaging for all viewers.
Final Review
Incorporating captions into your videos is a powerful way to enhance accessibility, improve viewer engagement, and meet legal standards. By mastering the various methods from creating caption files to uploading and customizing them across platforms, you can ensure your content is both professional and inclusive. Embracing these techniques will help you reach a wider audience and deliver your message effectively across diverse viewing contexts.